
CyberDefender: XWorm Lab Challenge Writeup
Description: Analyze malware behavior to identify persistence methods, evasion techniques, and C2 infrastructure by extracting artifacts and configuration data from static and dynamic analysis.
Challenge Link: https://cyberdefenders.org/blueteam-ctf-challenges/xworm/
Level: Medium
Category: Malware Analysis
Tactics: Execution, Persistence, Privilege Escalation, Defense Evasion, Credential Access, Discovery, Collection
Tools: Detect It Easy, CFF Explorer, PEStudio, dnSpy, ProcMon, RegShot, Python3
Scenario
An employee accidentally downloaded a suspicious file from a phishing email. The file executed silently, triggering unusual system behavior. As a malware analyst, your task is to analyze the sample to uncover its behavior, persistence mechanisms, communication with Command and Control (C2) servers, and potential data exfiltration or system compromise.
Questions
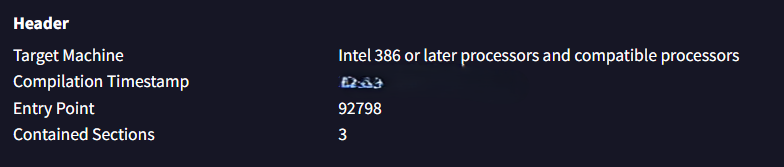
Q1: What is the compile timestamp (UTC) of the sample?
Solution: 2024-02-25 22:53
Upon uploading the XWorm malware file to VirusTotal, the compilation timestamp can be found in the Header section within the Details tab.
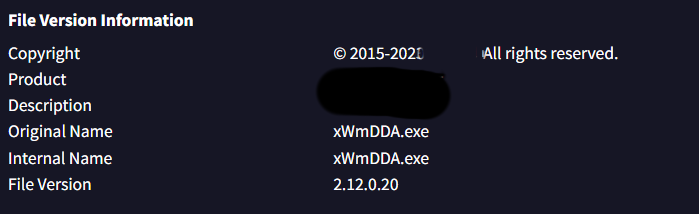
Q2: Which legitimate company does the malware impersonate in an attempt to appear trustworthy?
Solution: Adobe
The legitimate company information can be found in the File Version Information section within the Details tab on VirusTotal.
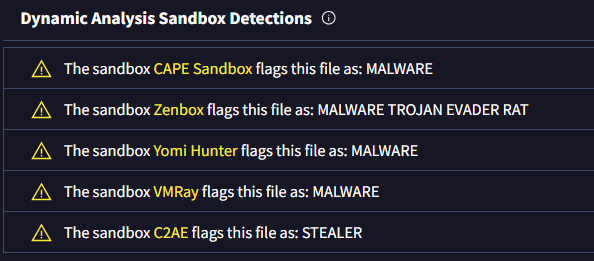
Q3: How many anti-analysis checks does the malware perform to detect/evade sandboxes and debugging environments?
Solution: 5
In the Behavior tab, under the Dynamic Analysis — Sandbox Detections section, I observed several sandbox detection techniques and counted how many were related to detection or evasion.
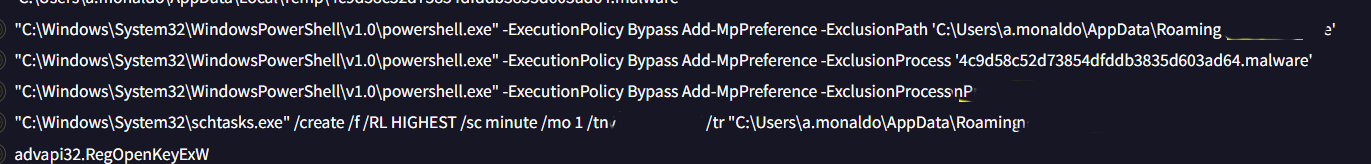
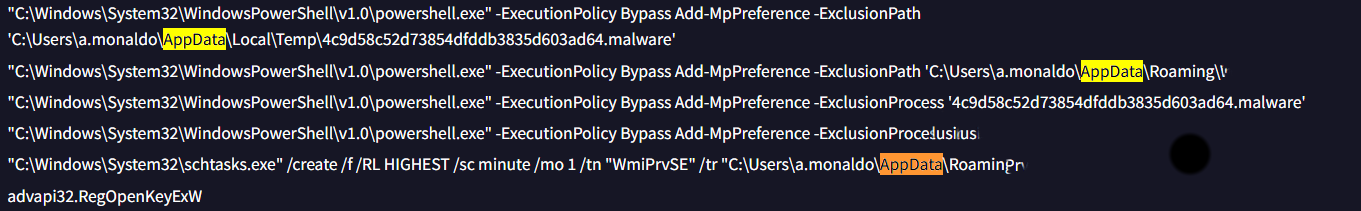
Q4: What is the name of the scheduled task created by the malware to achieve execution with elevated privileges?
Solution: WmiPrvSE
Upon deeper inspection of the Behavior tab, I identified scheduled tasks executing powershell.exe with commands designed to achieve elevated privileges.
Q5: What is the filename of the malware binary that is dropped in the AppData directory?
Solution: WmiPrvSE.exe
While analyzing the AppData directory entries in the Behavior tab, I observed that the scheduled task and the malware binary filename contain similar patterns or naming conventions.
Q6: Which cryptographic algorithm does the malware use to encrypt or obfuscate its configuration data?
Solution: AES
During a more detailed analysis of the Behavior tab, I discovered a significant Decoded Text section containing key information related to encryption and other relevant details.
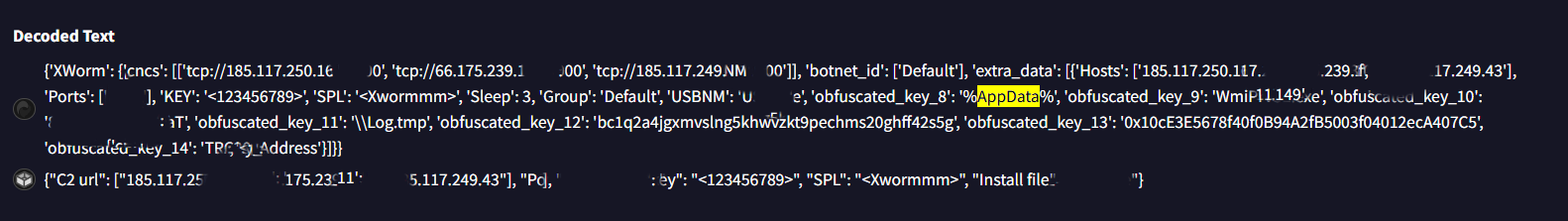
Q7: To derive the parameters for its encryption algorithm, the malware uses a hardcoded string as input. What is the value of this hardcoded string?
Solution: 8xTJ0EKPuiQsJVaT
Q8: What are the Command and Control (C2) IP addresses obtained after the malware decrypts them?
Solution: 185.117.250.169, 66.175.239.149, 185.117.249.43
Q9: What port number does the malware use for communication with its Command and Control (C2) server?
Solution: 7000
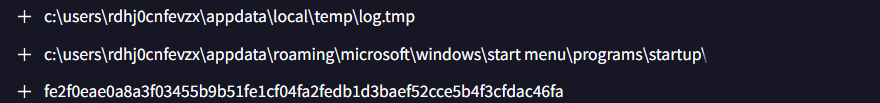
Q10: The malware spreads by copying itself to every connected removable device. What is the name of the new copy created on each infected device?
Solution: usb.exe
Q11: To ensure its execution, the malware creates specific types of files. What is the file extension of these created files?
Solution: lnk
During my analysis of the Behavior tab, I identified a file in link format, which appears to be used for linking to malicious files or initiating suspicious processes.
Q12: What is the name of the DLL the malware uses to detect if it is running in a sandbox environment?
Solution: SbieDll.dll
This detail is not present in VirusTotal but was discovered through manual analysis using CFF Explorer or DLLRunner.
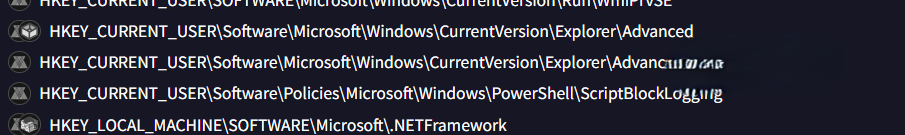
Q13: What is the name of the registry key manipulated by the malware to control the visibility of hidden items in Windows Explorer?
Solution: ShowSuperHidden
While examining the Registry Key section of the Behavior tab for references to Windows Explorer, I identified a registry key associated with configuring the visibility of hidden files and folders.
Q14: Which API does the malware use to mark its process as critical in order to prevent termination or interference?
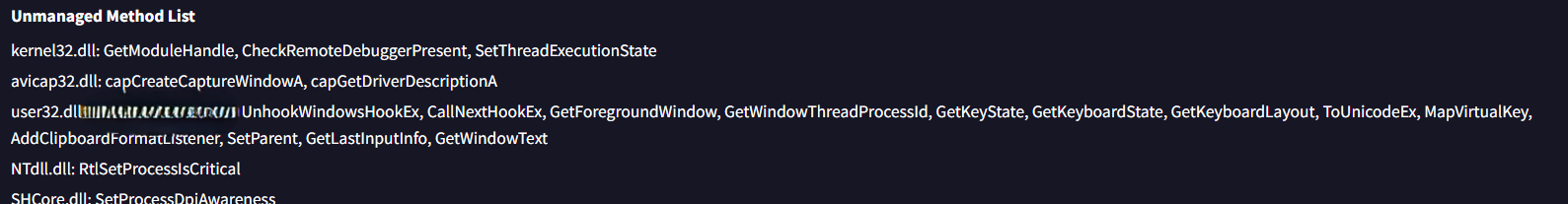
Solution: RtlSetProcessIsCritical
During my analysis of the Details tab on VirusTotal, I observed an Unmanaged Methods list containing various API functions. One of these functions is used by the malware to mark its process as critical.
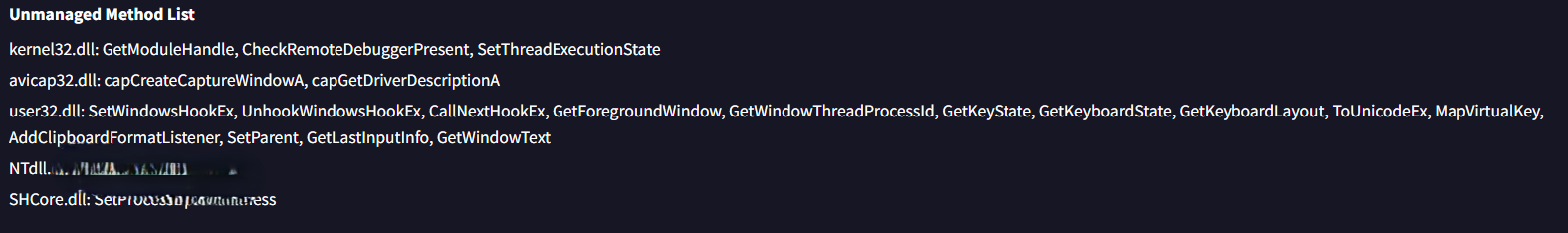
Q15: Which API does the malware use to insert keyboard hooks into running processes in order to monitor or capture user input?
Solution: SetWindowsHookEx
Additionally, within the Unmanaged Methods section, I observed that the malware employs functions to insert keyboard hooks into active processes.
Q16: Given the malware’s ability to insert keyboard hooks into running processes, what is its primary functionality or objective?
Solution: Keylogger
During my analysis of the Unmanaged Methods list, I identified a function typically associated with monitoring keyboard input. One well-known tool capable of such keyboard activity monitoring is ____.
Conclusion
During the analysis of the XWorm malware using VirusTotal and other tools like CFF Explorer and DLLRunner, I identified several malicious behaviors. The Details tab revealed a compilation timestamp and impersonation of a legitimate company, enhancing the malware’s credibility. The Behavior tab showed evidence of sandbox detection, scheduled tasks executing powershell.exe with elevated privileges, and activity within the AppData directory suggesting persistence mechanisms.
Further inspection uncovered a Link file used to link malicious processes, and registry keys modifying Windows Explorer settings to hide files. The Unmanaged Methods list provided insight into API usage for marking the malware process as critical and inserting keyboard hooks for monitoring user input—techniques commonly associated with keyloggers.
These findings helped answer multiple questions by highlighting key behaviors such as process protection, user surveillance, and persistence techniques, underscoring the sophisticated evasion and control strategies used by the malware.