
CyberDefender: Qradar101 Lab Challenge Writeup
Description: Analyze diverse log sources in QRadar SIEM to identify compromised systems, detect malicious tools, and reconstruct the sequence of attack events.
Level: Medium
Category: Threat Hunting
Link: https://cyberdefenders.org/blueteam-ctf-challenges/qradar101/
Tactics: Execution, Persistence, Privilege Escalation, Defense Evasion, Discovery, Lateral Movement, Collection, Command and Control, Exfiltration
Tools: QRadar
Scenario
A financial company was compromised, and they are looking for a security analyst to help them investigate the incident. The company suspects that an insider helped the attacker get into the network, but they have no evidence.
The initial analysis performed by the company's team showed that many systems were compromised. Also, alerts indicate the use of well known malicious tools in the network. As a SOC analyst, you are assigned to investigate the incident using QRadar SIEM and reconstruct the events carried out by the attacker.
Instructions:
- Compatibility: VirtualBox
- Uncompress the lab (
pass: cyberdefenders.org) - Zip SHA1:
7d2e0b18bc11e9987431369b180577886d956b0a - Zip size: 20 GB
- Please make sure to watch the instructional video under the Walkthroughs section.
- Make sure you have a host-only subnet within the following IP range
192.168.20.0/24. - Assign the proper network adapter (
192.168.20.0/24) to the VM before starting it. - Wait for some minutes after the import completes then visit:
https://192.168.20.21/. - Challenge credentials: QRadar Dashboard:
admin:Admin@123- SSH:root:cyberdefenders - In case you face a license issue, please go to > License Pool Management. Edit and set eps > 0 and edit the FPM and set it to 0. This will ensure you will not have a license problem.
- Hardware Requirements:
8GB of memory and 65GB of disk space.
Dataset:
- Sysmon - swift on security configuration
- Powershell logging
- Windows Eventlog
- Suricata IDS
- Zeek logs (conn, HTTP)
Questions
Q1. How many log sources available?
Solution: 15.
Step 1: Select Admin -> Data Source -> Log Sources.
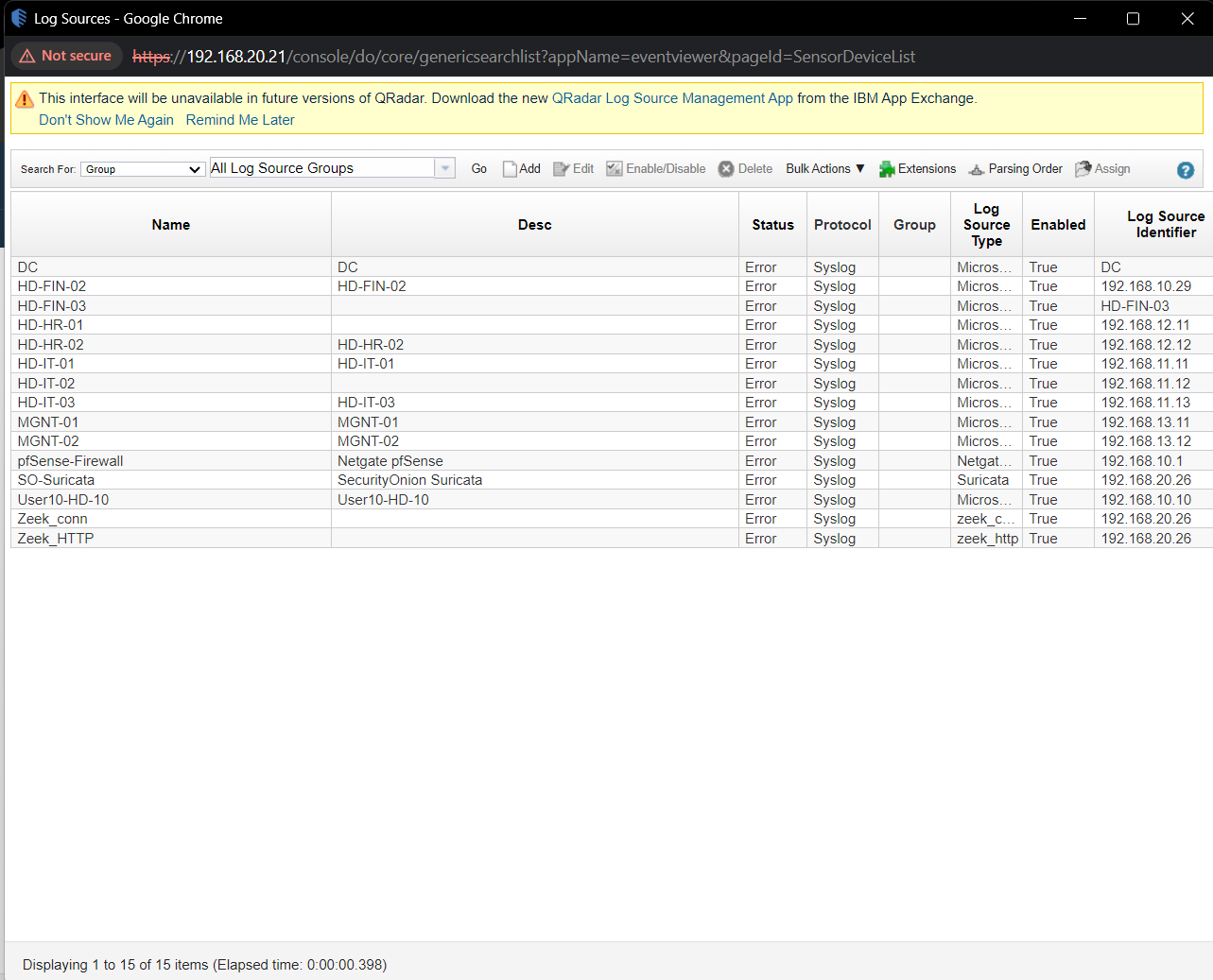
Step 2: Counting log Items.

Q2. What is the IDS software used to monitor the network?
Solution: Suricata.
Step 1: Select Admin -> Data Source -> Log Sources.
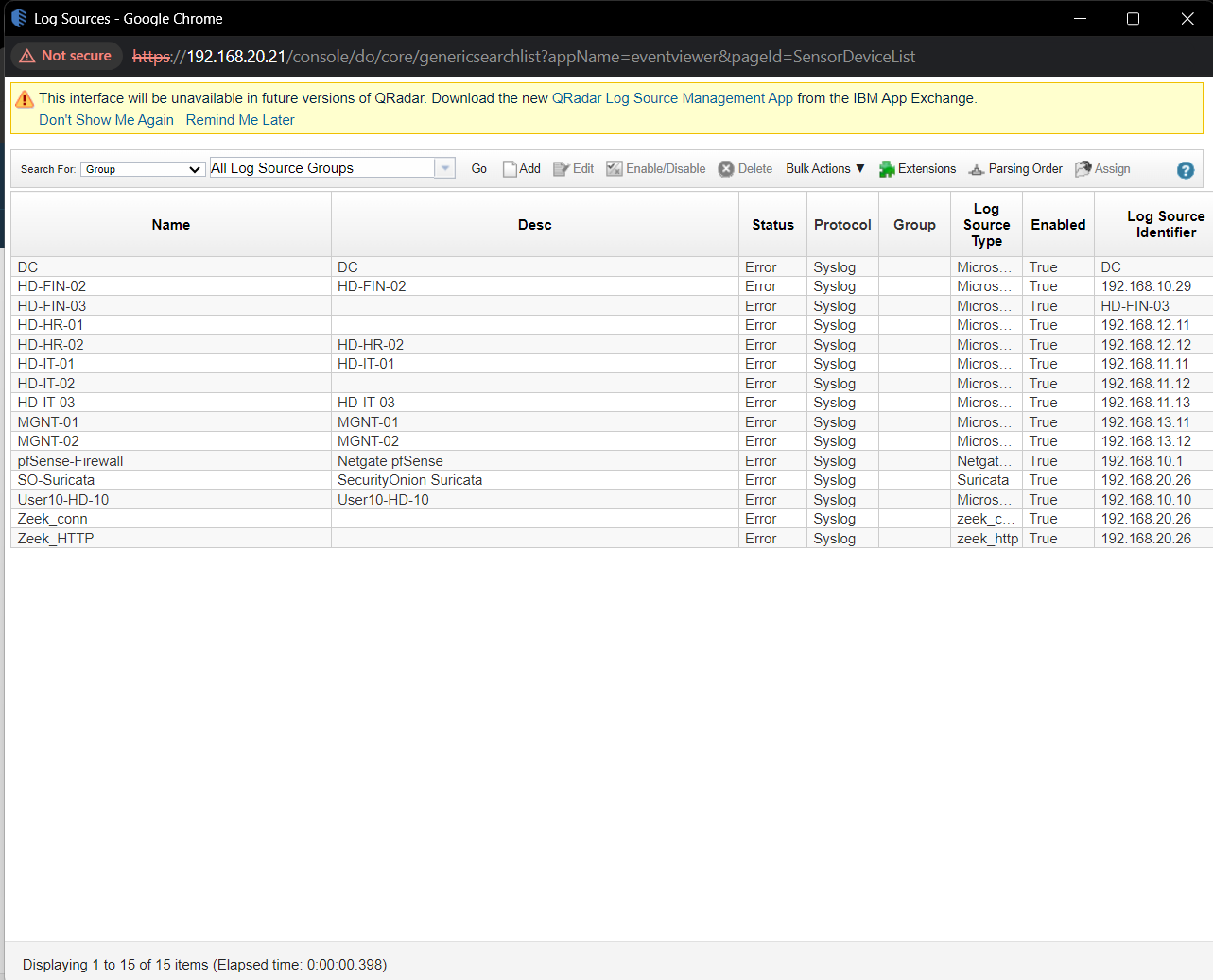
Step 2: Find the IDS software which used for monitor the network

Q3. What is the domain name used in the network?
Solution: HACKDEFEND.local.
Step 1: Select Log Activity -> Search Log Activity then Find Log Between 10/23/2020 to 11/16/2020 and Start Quick Search h*.l*.
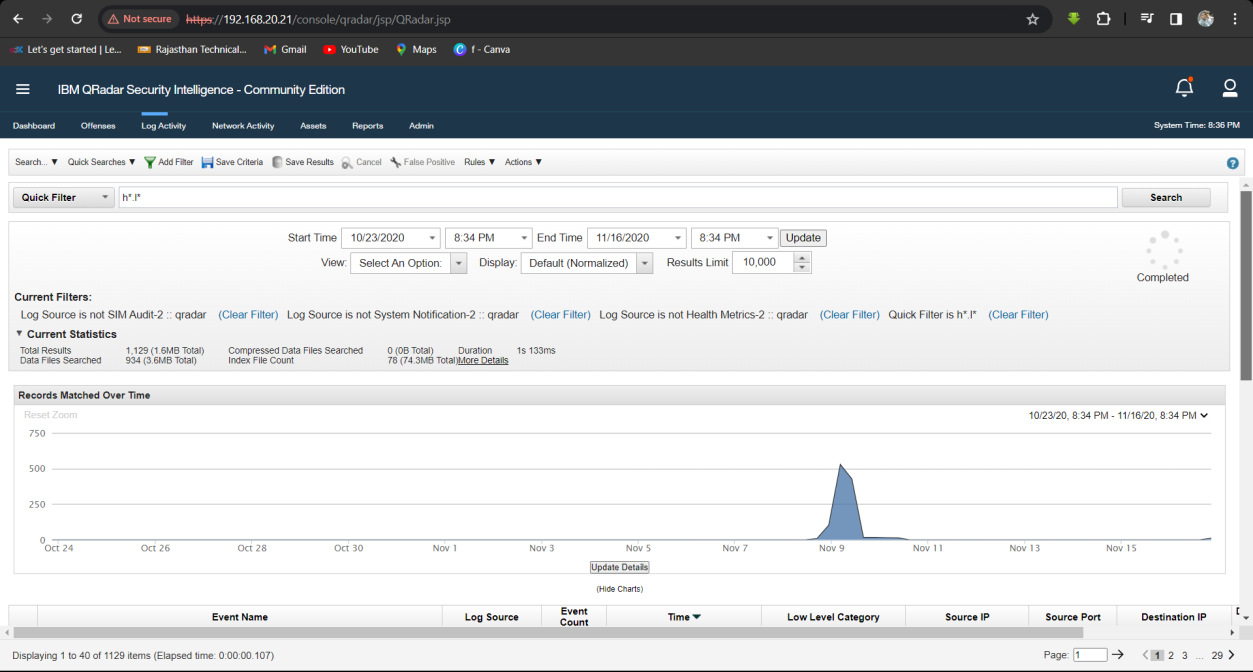
Step 2: Open First Log Activity File.
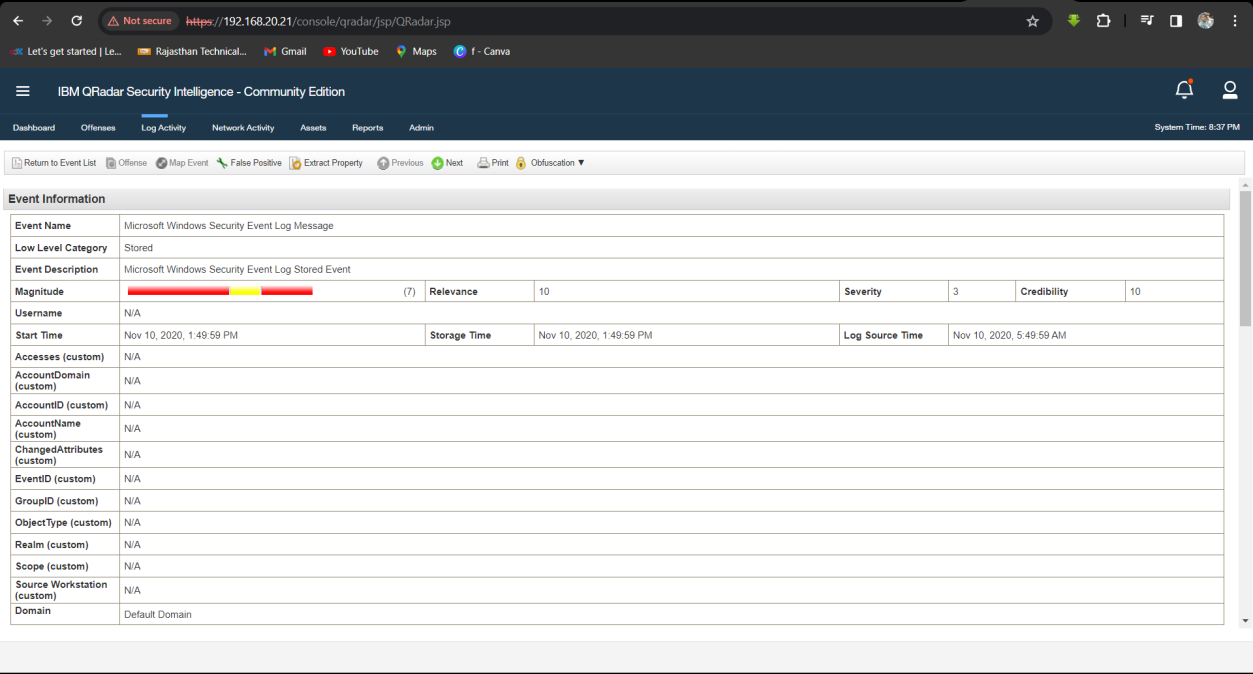
Step 3: Scroll Down then Find Domain Name in Payload Information.
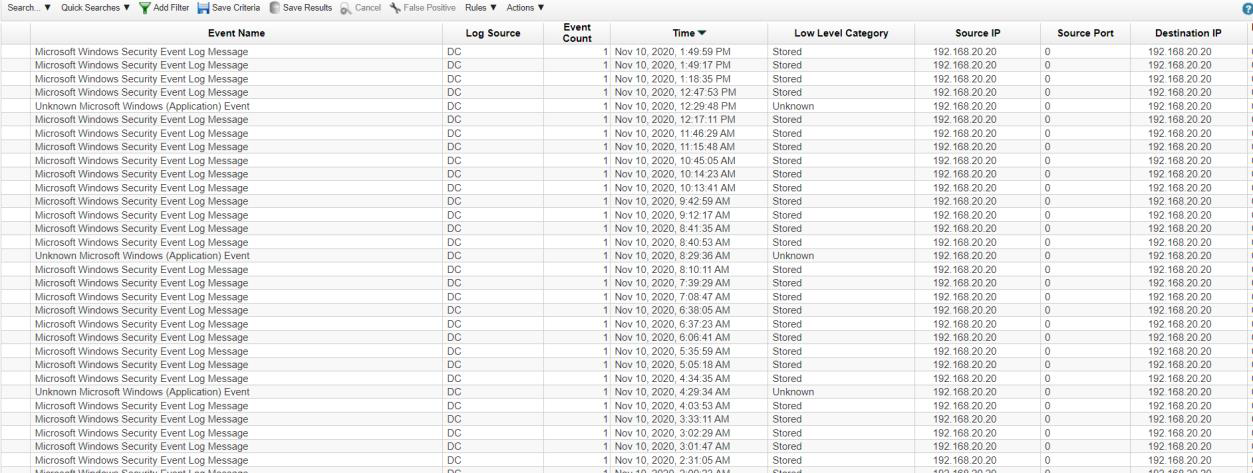
Q4. Multiple IPs were communicating with the malicious server. One of them ends with "20". Provide the full IP.
Solution: 192.168.20.20.
Step 1: Observe Log Activity between 10/23/2020 to 11/16/2020 then we find out that malicious IP 192.168.20.20.
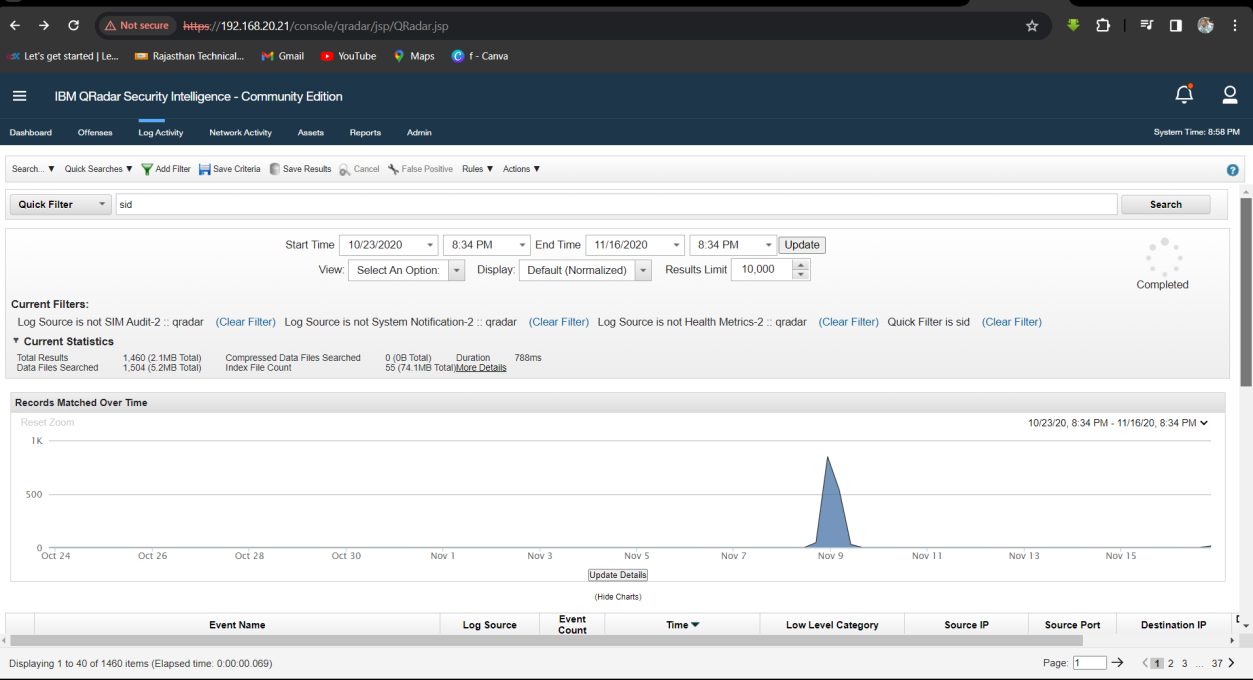
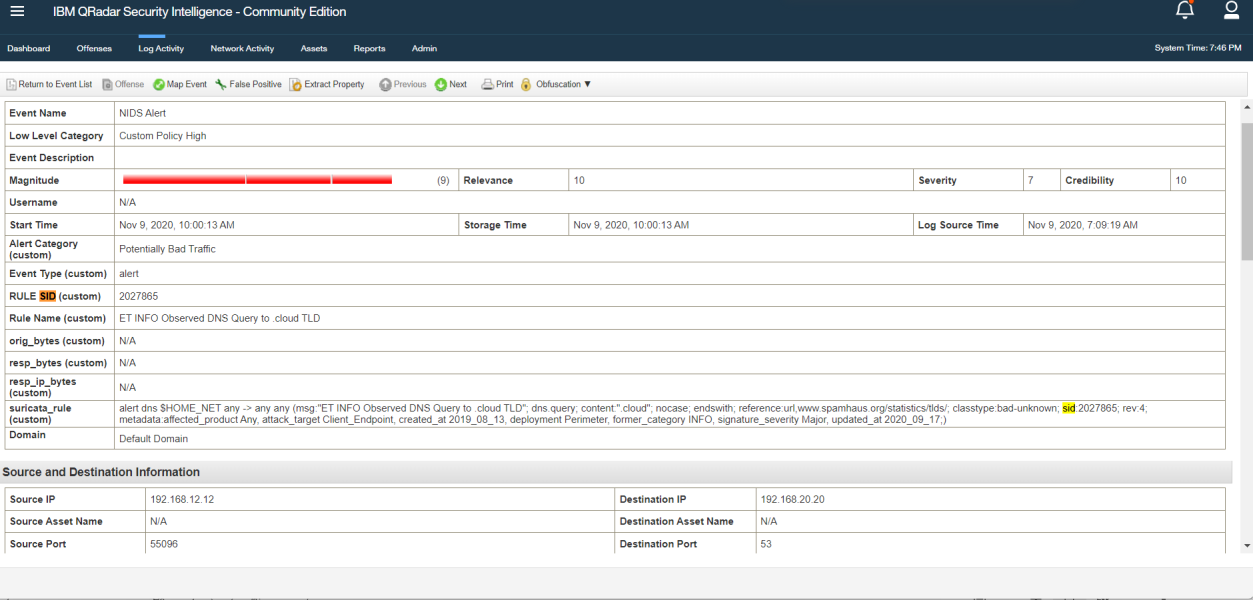
Q5. What is the SID of the most frequent alert rule in the dataset?
Solution: 2027865.
Step 1: Select Log Activity -> Search Log Activity and Find Log Between 10/23/2020 to 11/16/2020 then Start Quick Search sid.
Step 2: Open NIDS Alert Log Activity.
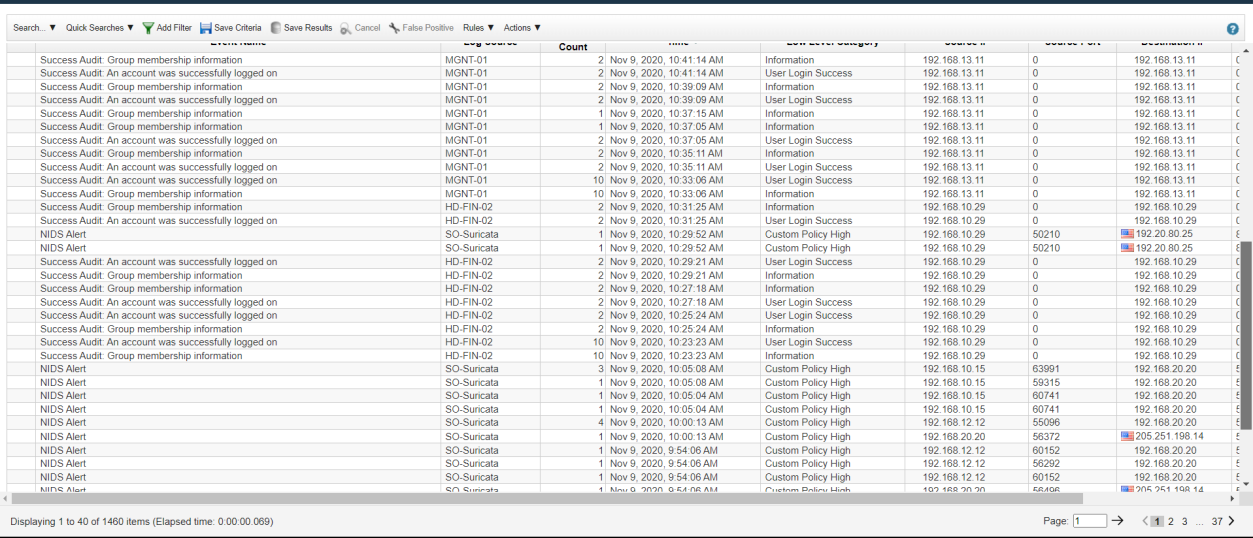
Step 3: Find 110 logs from SO-Suricata where 72 is 2027865
Q6. What is the attacker's IP address?
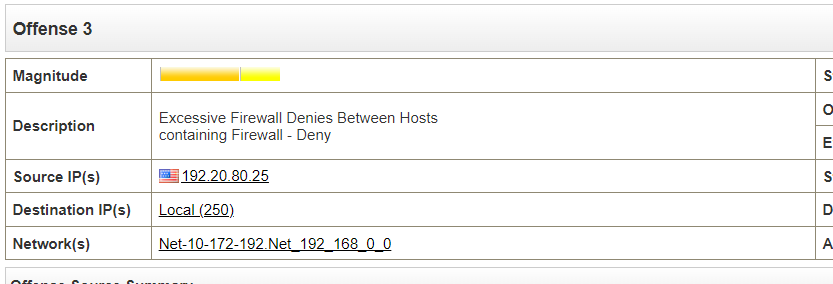
Solution: 192.20.80.25.
Step 1: Select offence -> Clear Hidden Filter then Show some Log Activity.
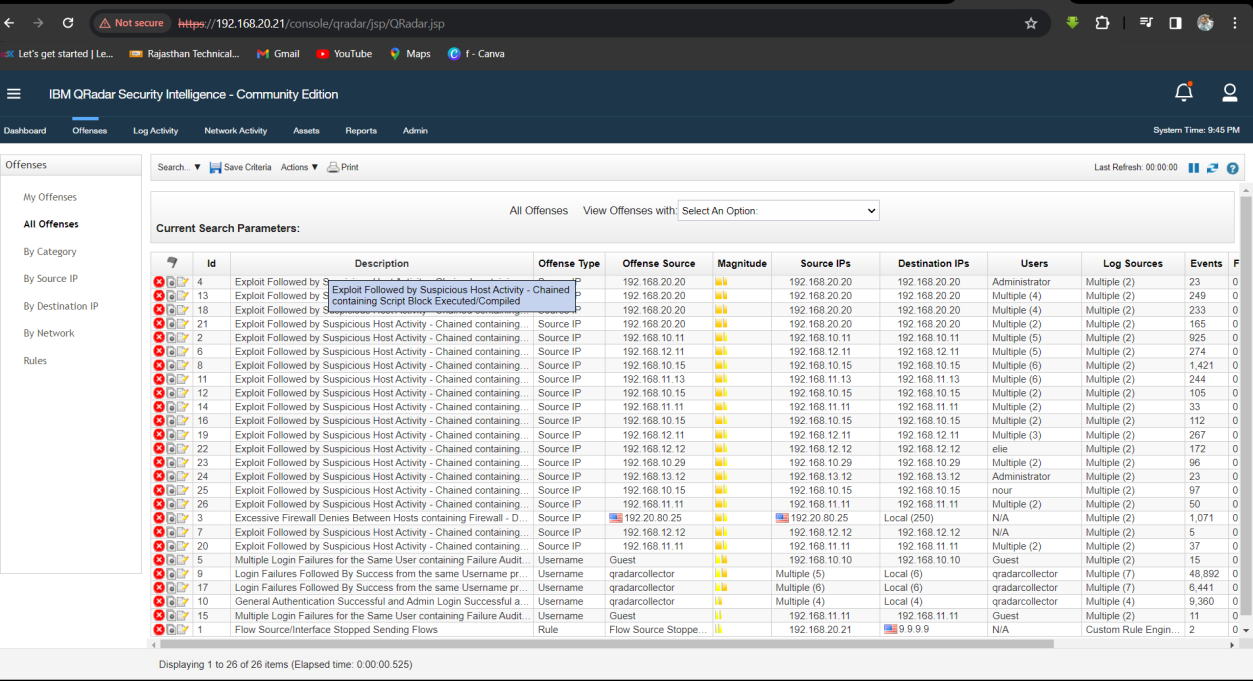
Step 2: Analyse the Activity event then find the Attacker’s address in Offence 3 event.
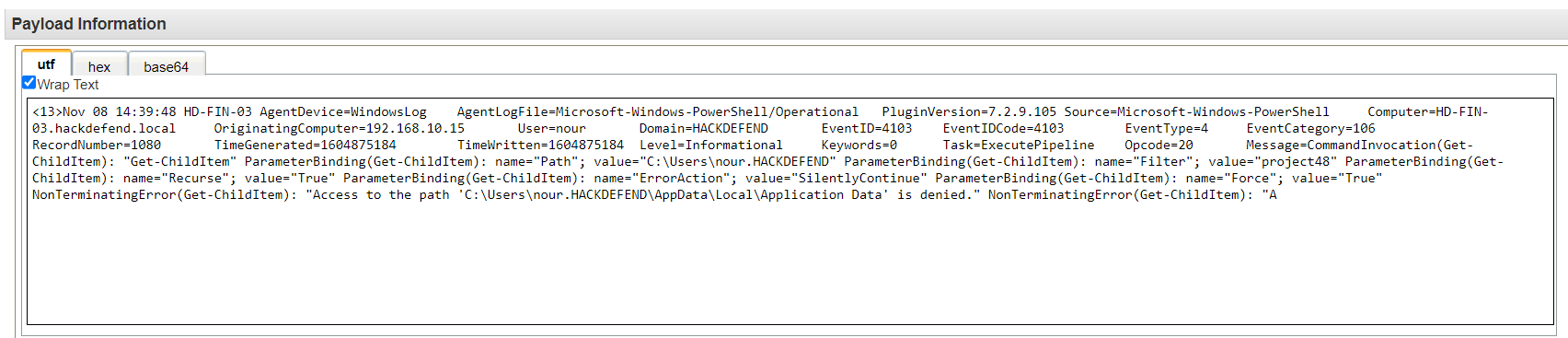
Q7. The attacker was searching for data belonging to one of the company's projects, can you find the name of the project?
Solution: project48.
Step 1: Select Log Activity -> Add Filter Payload Matches Regular Expression is Project
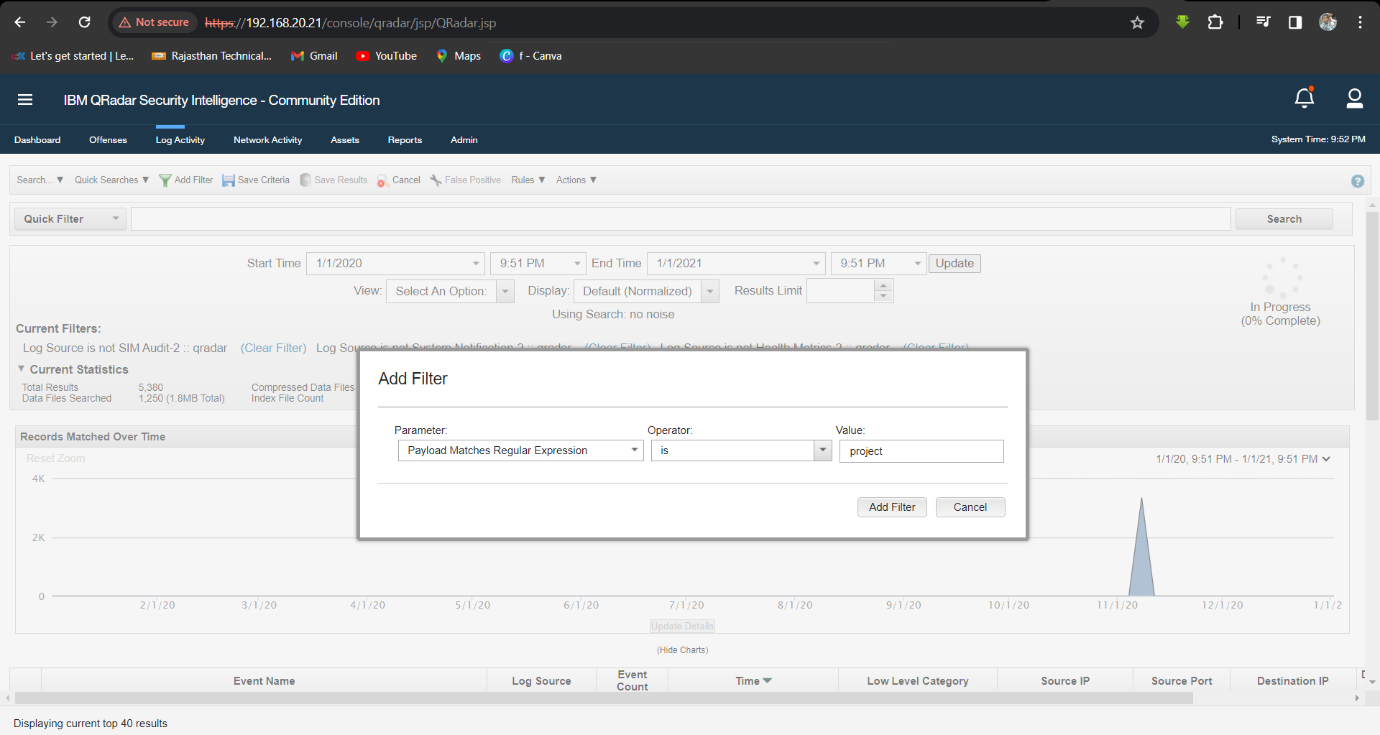
Step 2: Four Result are Show. Analyse the Result.

Step 3: In every Log Activity find Project48.
Q8. What is the IP address of the first infected machine?
Solution: 192.168.10.15.
Step 1: Select Log Activity -> Search Log Activity and Find Log Between 1/1/2020 to 1/1/2021.
Step 2: Click on Time Tag then Analyse the Log Activity.
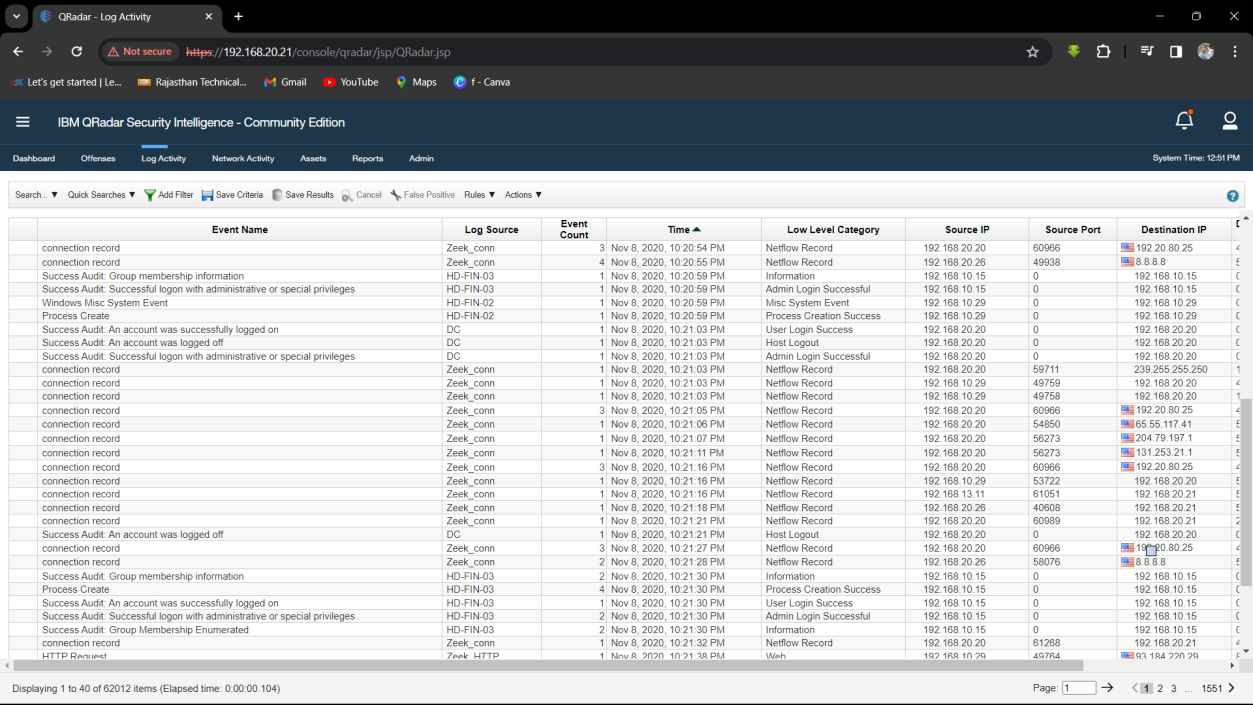
Step 3: Find Log Activity which used for Admin Login.

Step 4: Find the First infected Machine.
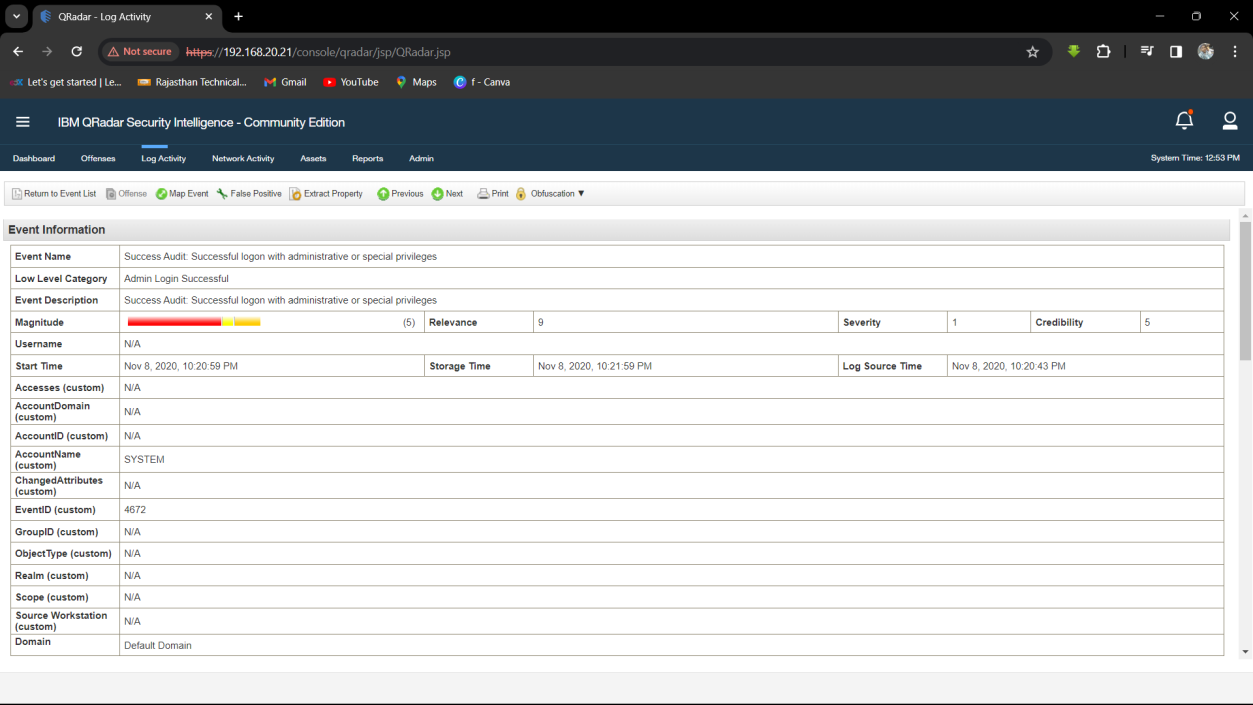
Q9. What is the username of the infected employee using 192.168.10.15?
Solution: nour.
Step 1: Select Log Activity -> Add Filter Source IP (index) is 192.168.10.15. Then Analyse the Log Activity. After Some Log files we find useful event Success Audit: Group Membership Enumerated
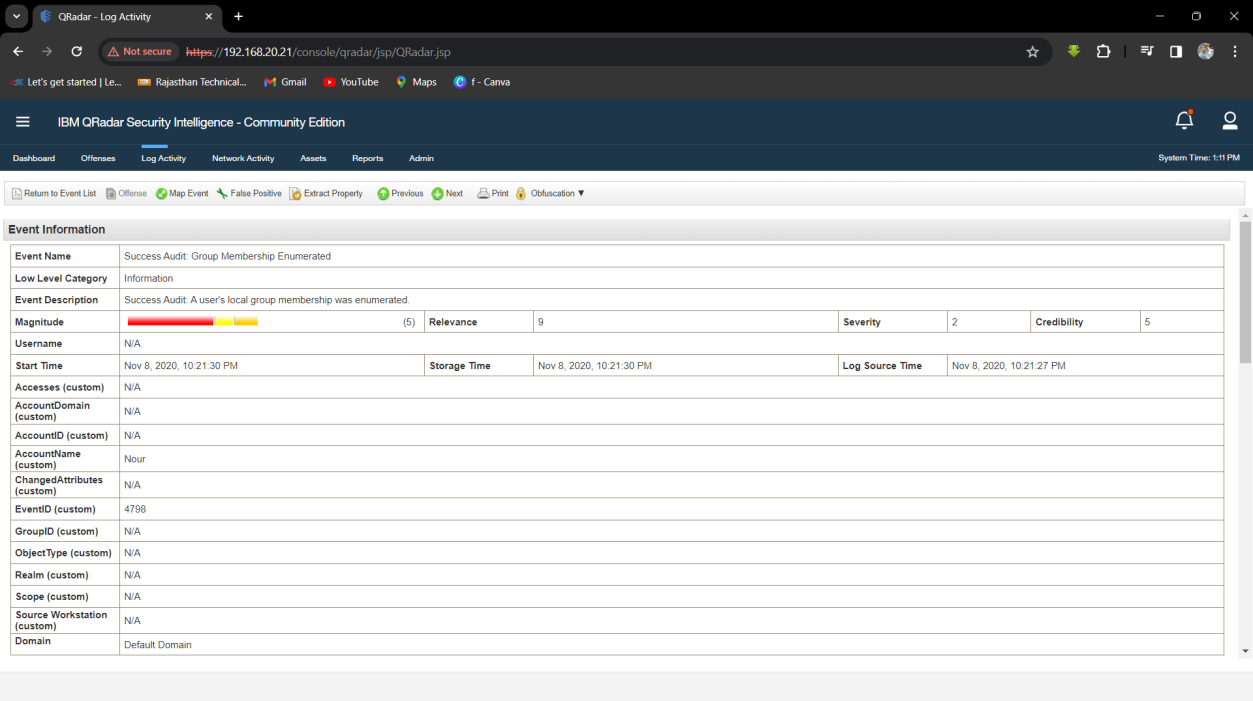
Step 2: Find Username is Nour.
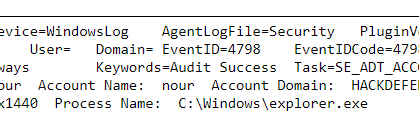
Q10. Hackers do not like logging, what logging was the attacker checking to see if enabled?
Solution: powershell.
Step 1: Select Log Activity -> Add Filter Payload Matches Regular Expression is Project48.
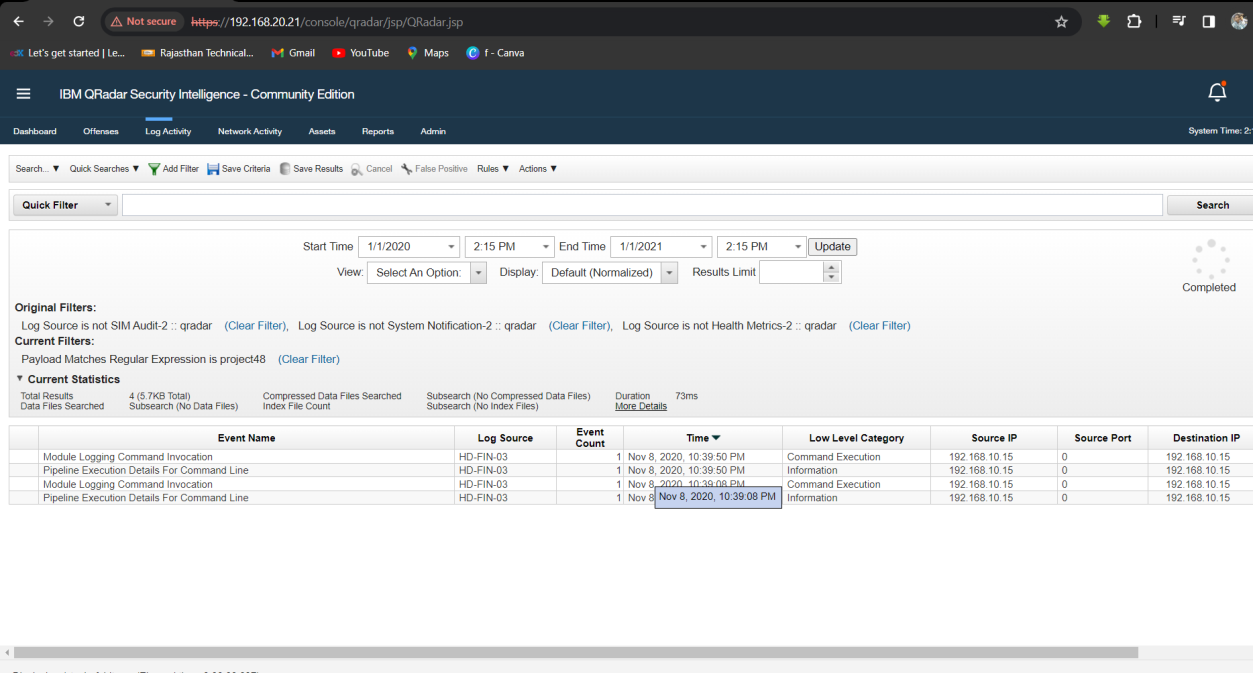
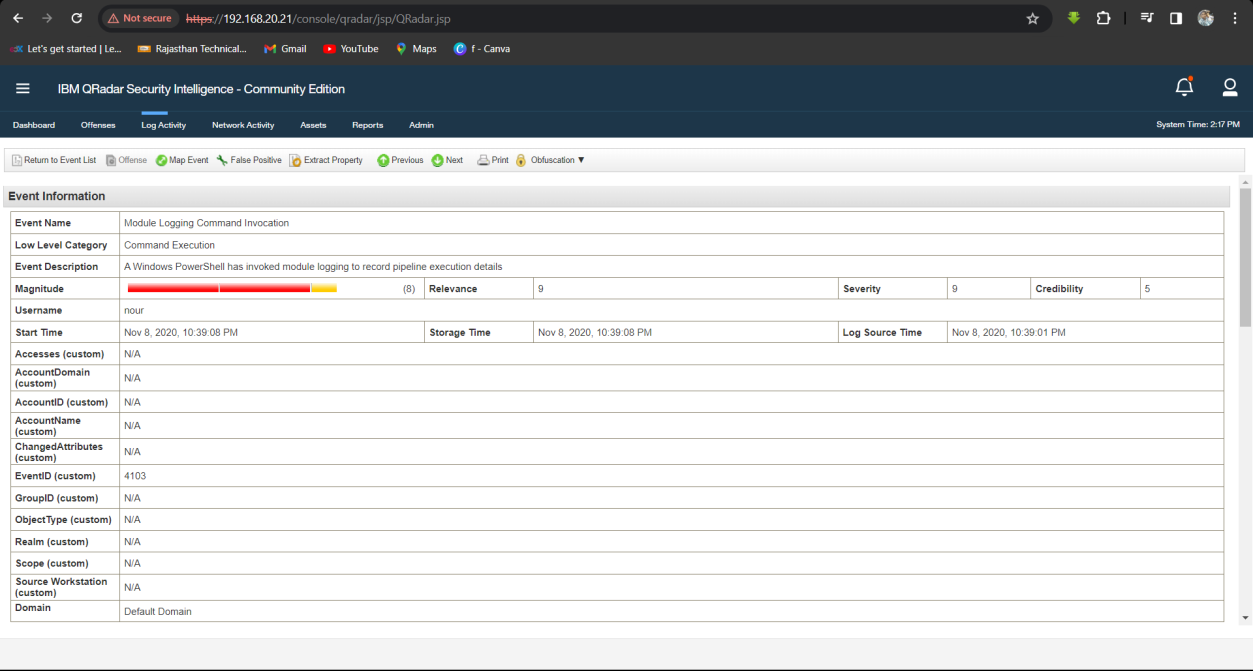
Step 2: Then Analyse the Log Activity event. In event Module Logging Command Invocation we find it.
Q11. Name of the second system the attacker targeted to cover up the employee?
Solution: MGNT-01.
Step 1: Select Log Activity -> Add Filter Payload Matches Regular Expression is del.
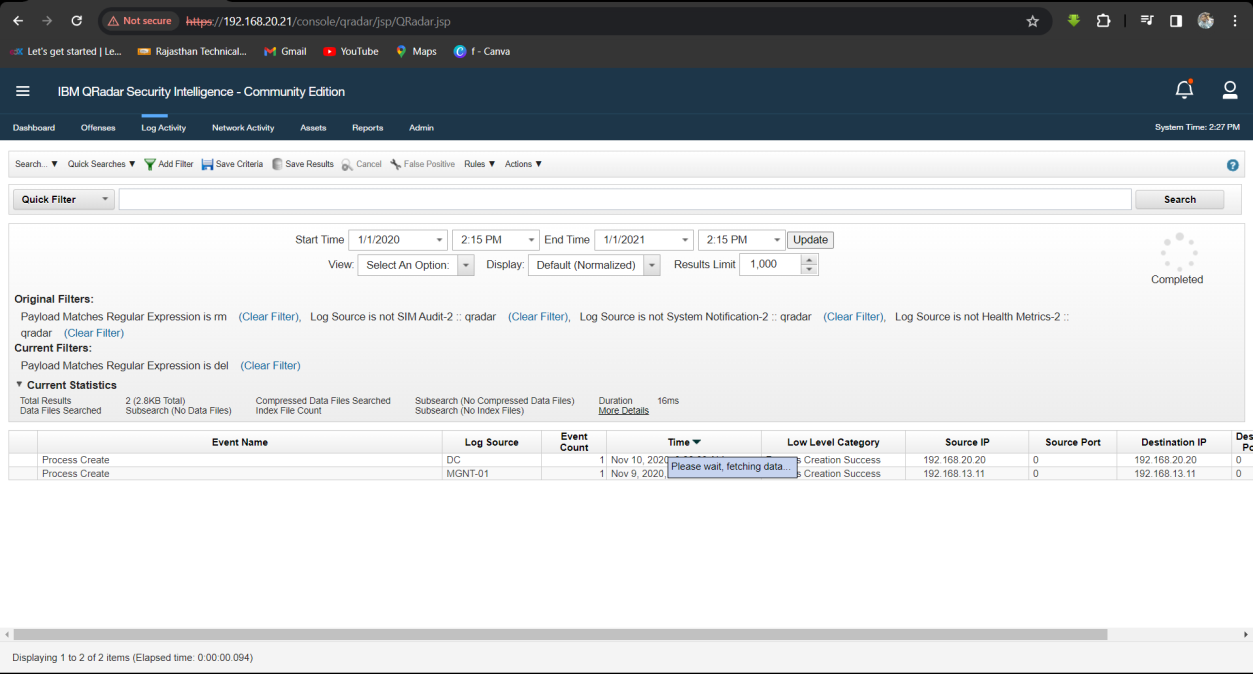
Step 2: Find the second System MGNT-01.
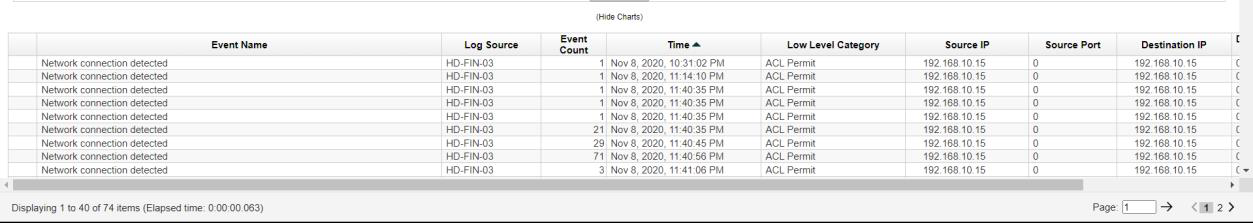
Q12. When was the first malicious connection to the domain controller (log start time - hh:mm:ss)?
Solution: 11:14:10.
Step 1: Select Log Activity -> Add Filter Event Name is Network connection detected.
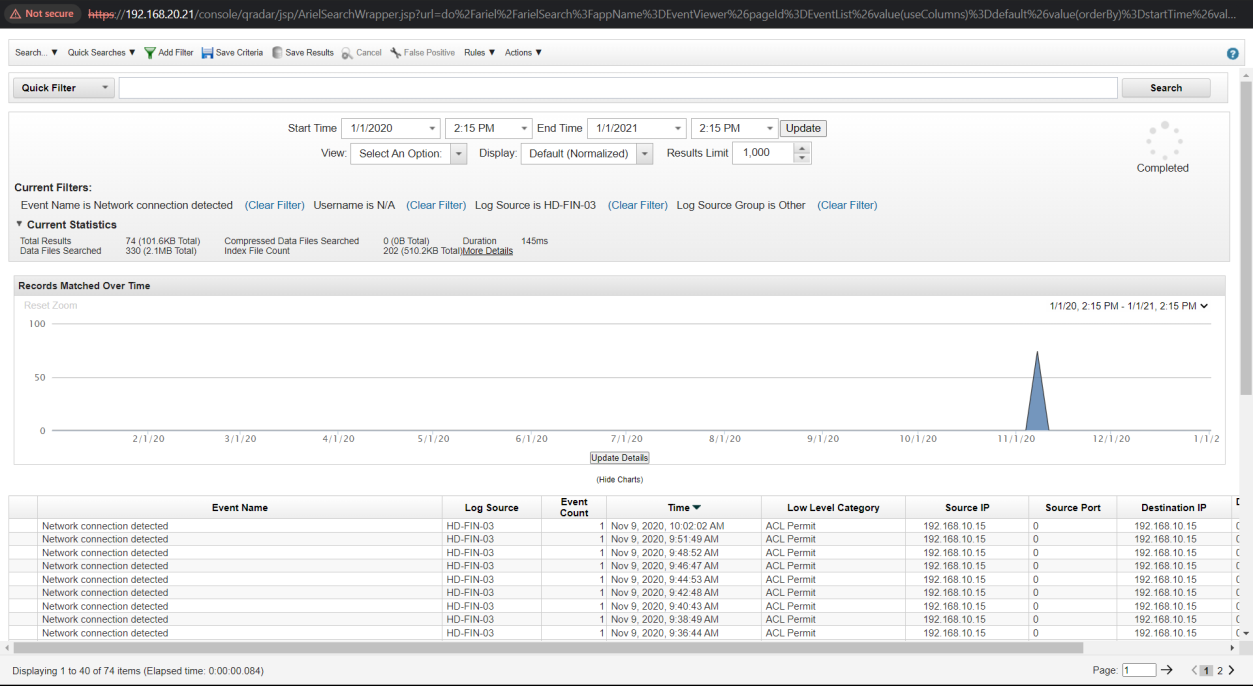
Step 2: Analyse the log start time.
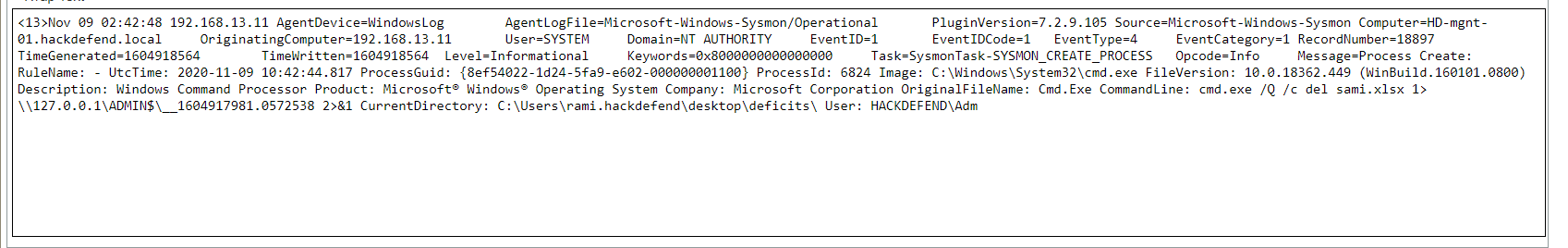
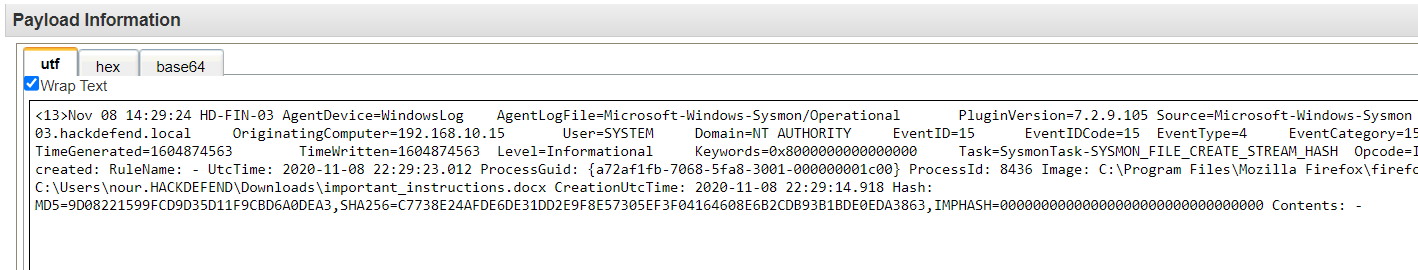
Q13. What is the md5 hash of the malicious file?
Solution: 9D08221599FCD9D35D11F9CBD6A0DEA3.
Step 1: Select Log Activity -> Add Filter Event Name is FileCreateStreamHash.
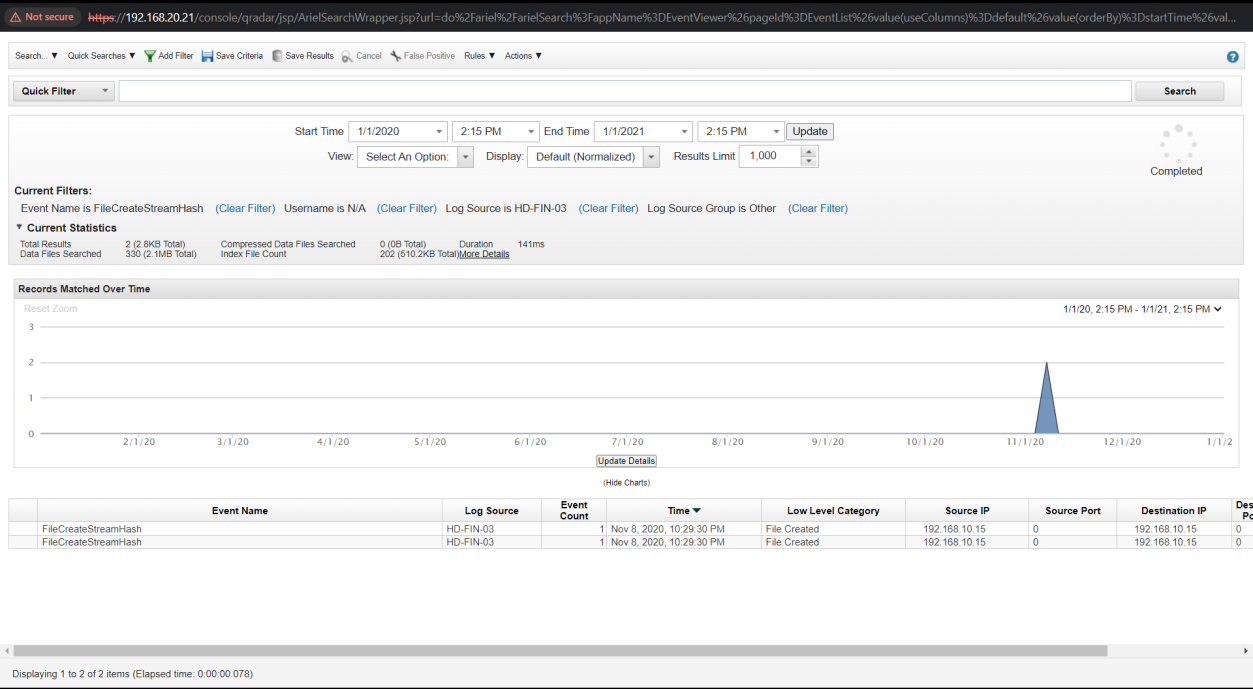
Step 2: Analyse the log event for MD5 hash.
Q14. What is the MITRE persistence technique ID used by the attacker?
Solution: T1547.001.
Step 1: Select Log Activity -> Add Filter Event Name is RegistryEvent (Value Set).
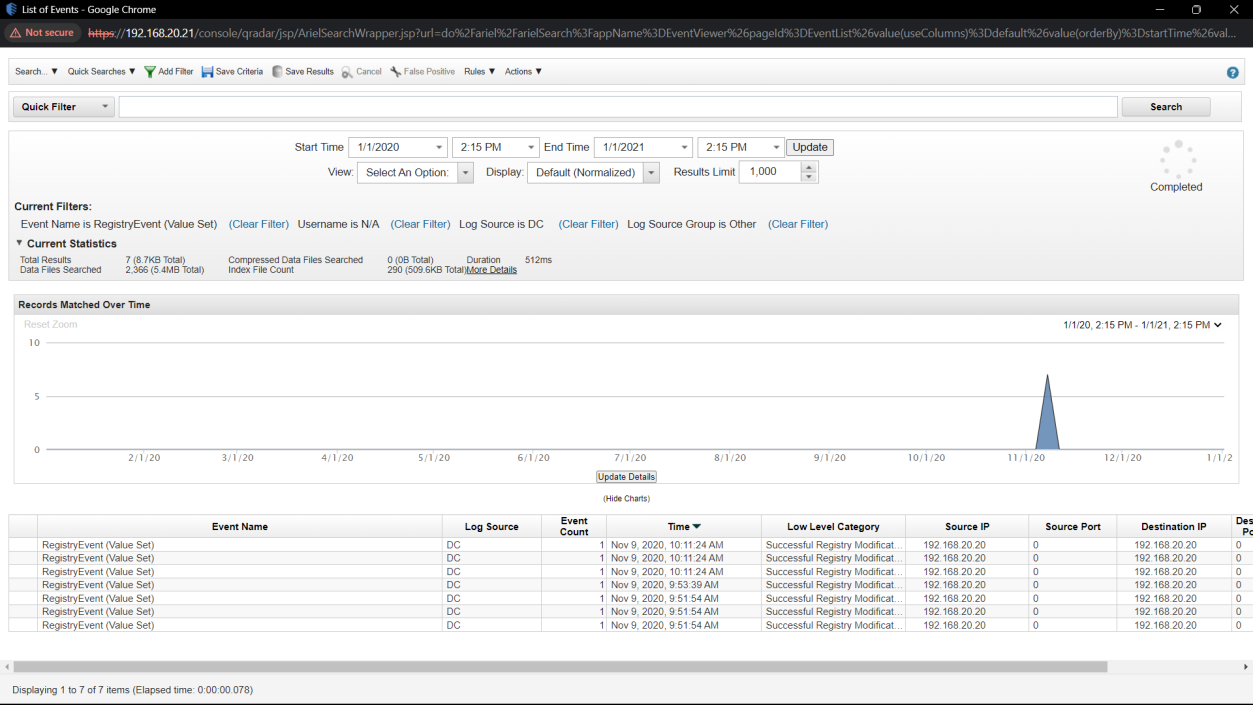
Step 2: Analyse the log event.
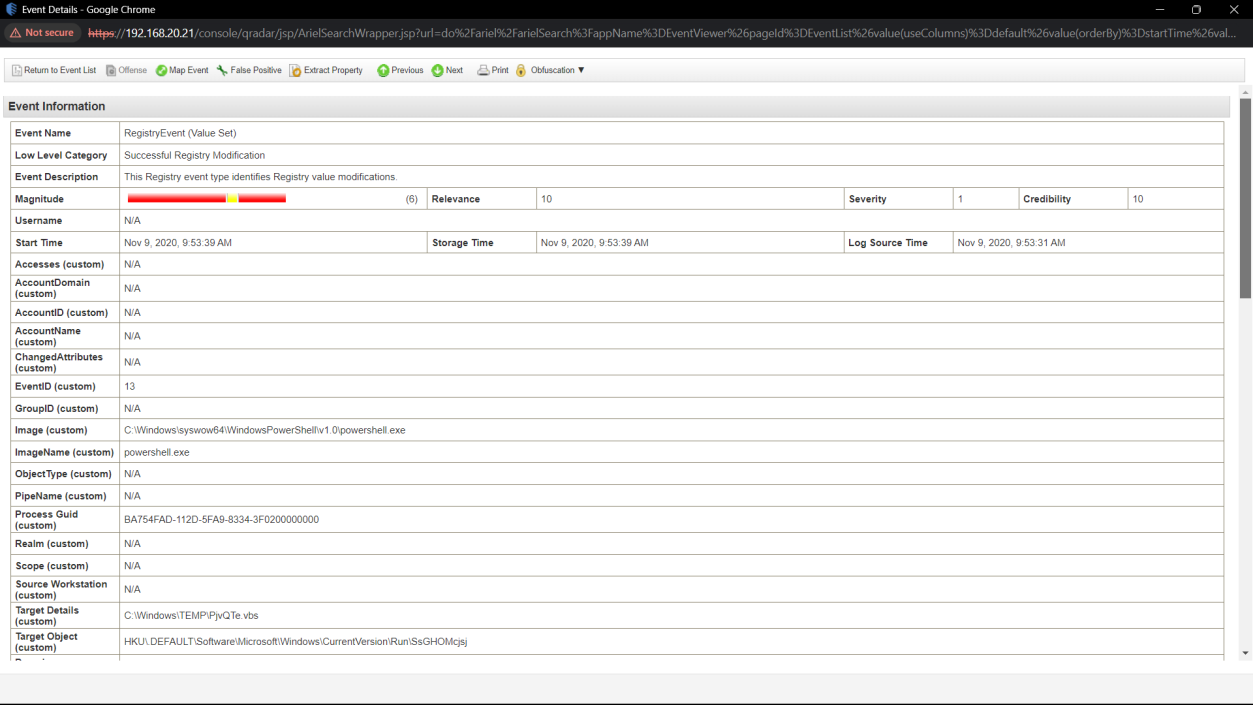
Step 3: Find the Rule name T1060 in Event.
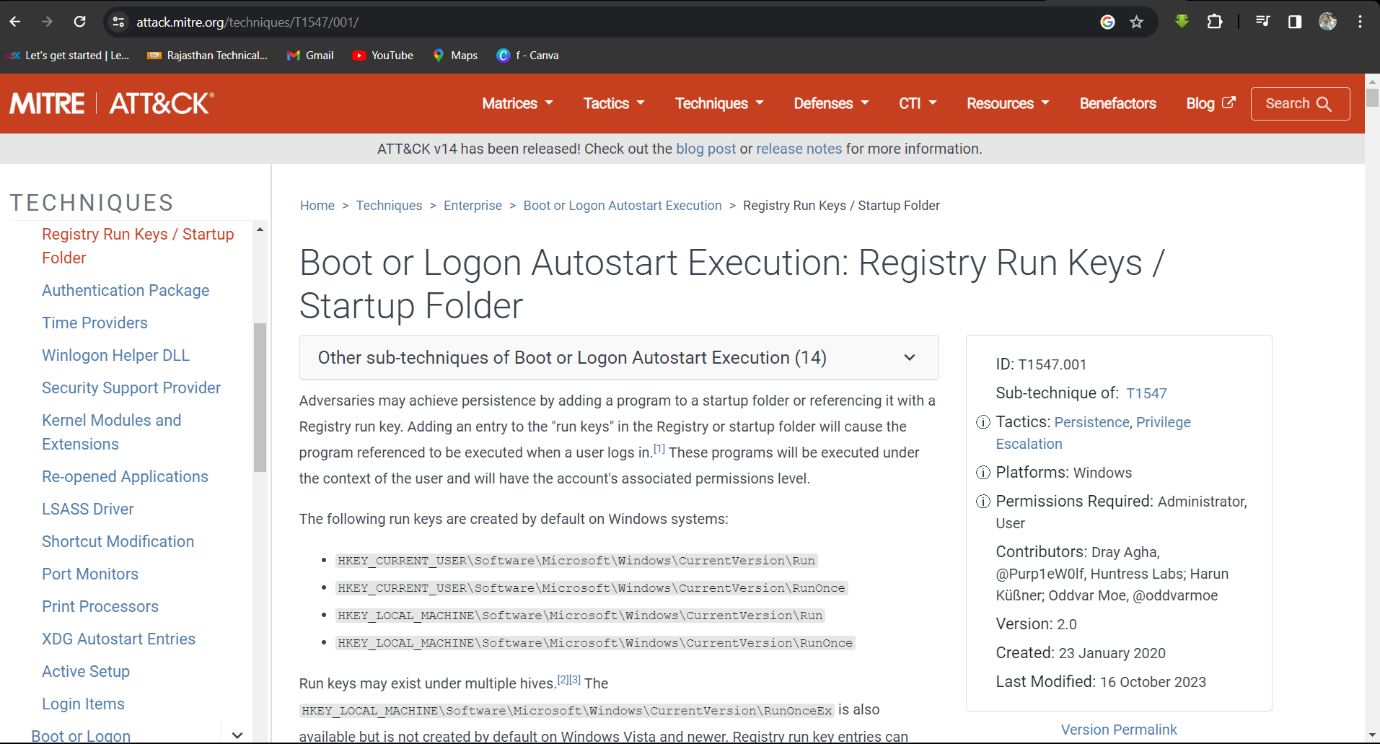
Step 4: Browser on google T1060 then find answer on this website.
https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1547/001/.
Q15. What protocol is used to perform host discovery?
Solution: icmp.
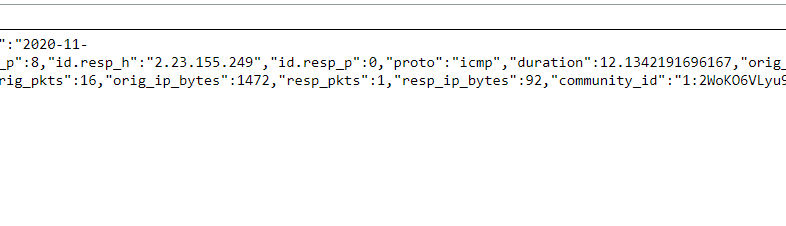
Step 1: Select Log Activity -> Add Filter Source IP is 192.168.10.15 and Log Source is Zeek_conn
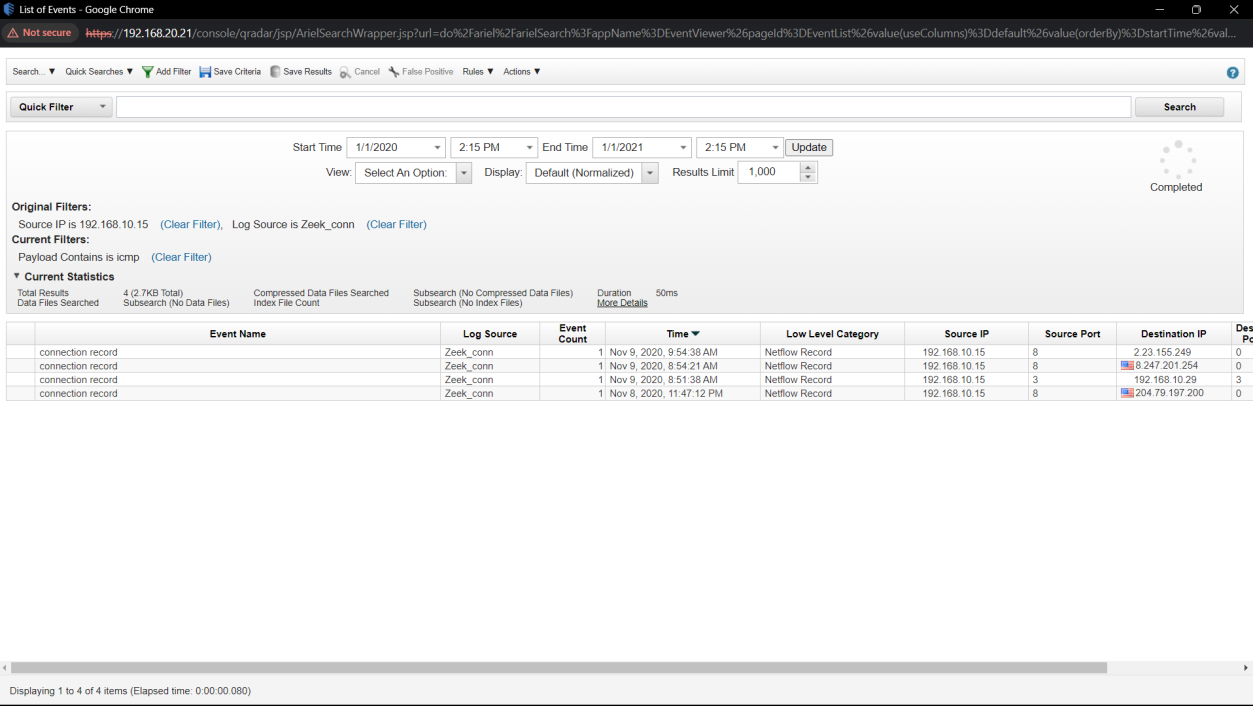
Step 2: Analyse the Event and Find the protocol which used for host discovery.
Q16. What is the email service used by the company?(one word)
Solution: Office365.
Step 1: Most IP belong to Microsoft So that it must be Microsoft service.
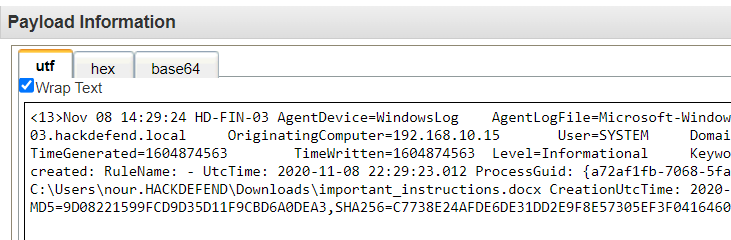
Q17. What is the name of the malicious file used for the initial infection?
Solution: important_instructions.docx.
Step 1: Select Log Activity -> Add Filter Event Name is FileCreateStreamHash.
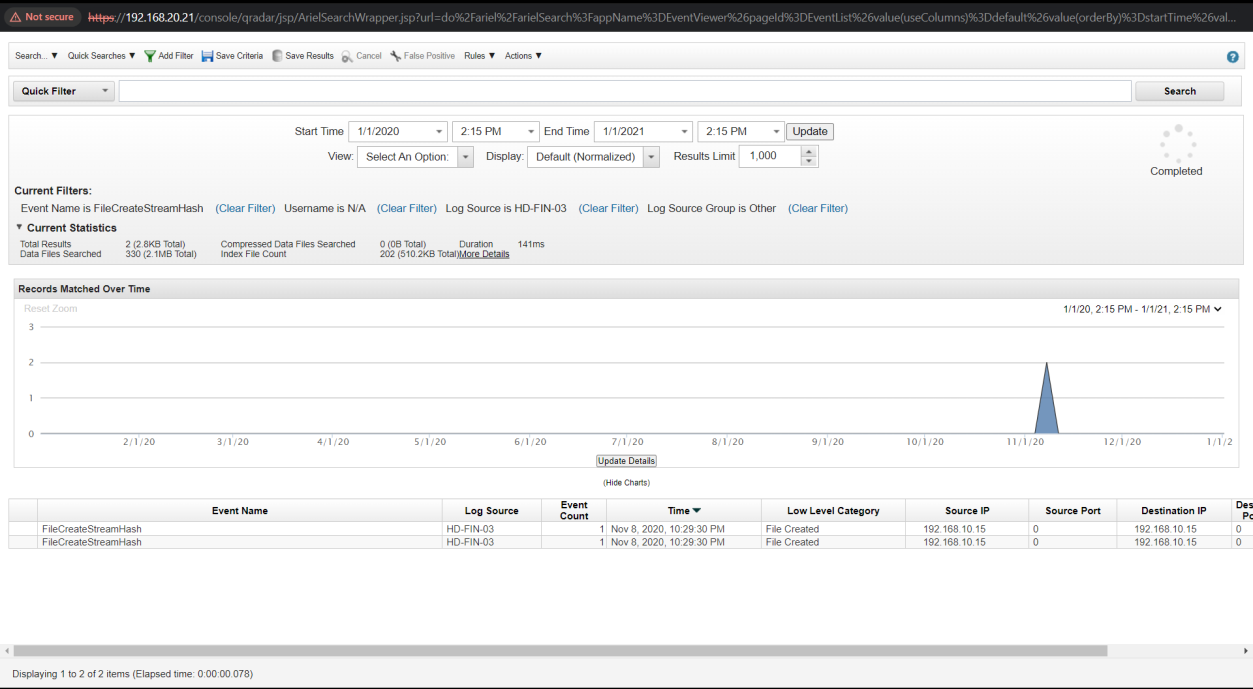
Step 2: Analyse the Log event for malicious file.
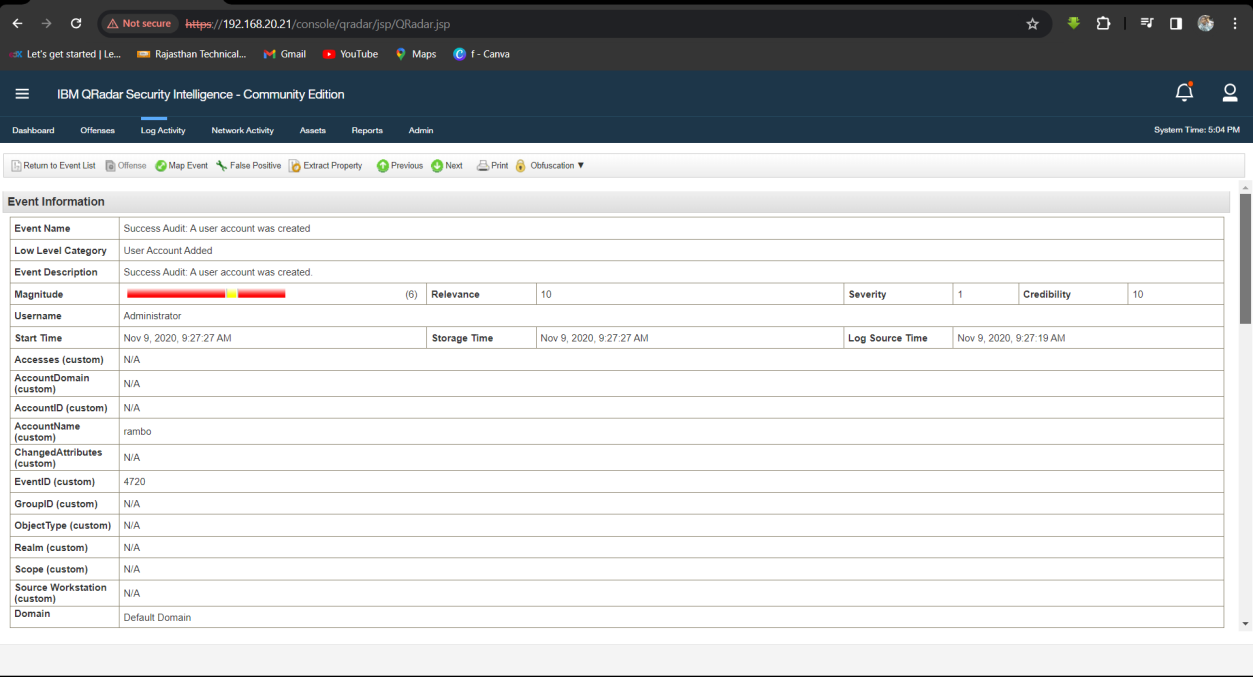
Q18. What is the name of the new account added by the attacker?
Solution: Rambo.
Step 1: Select Log Activity -> Add Filter Payload Contains is 4720.
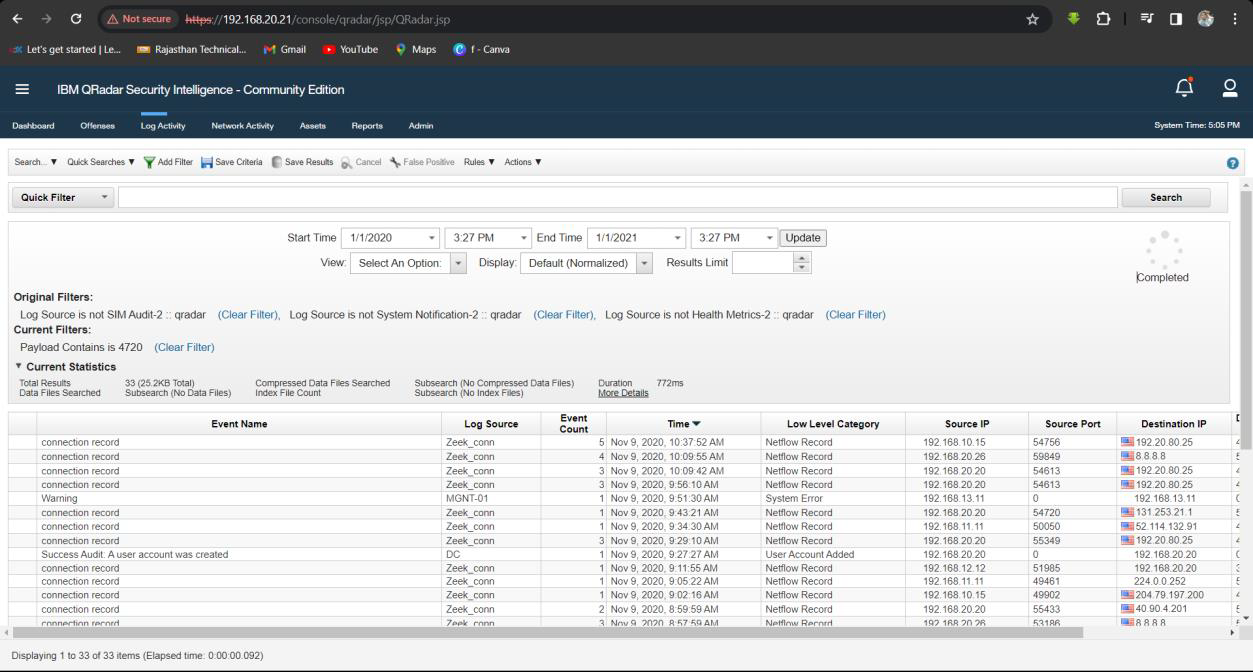
Step 2: Analyse the Log event for new Account name.

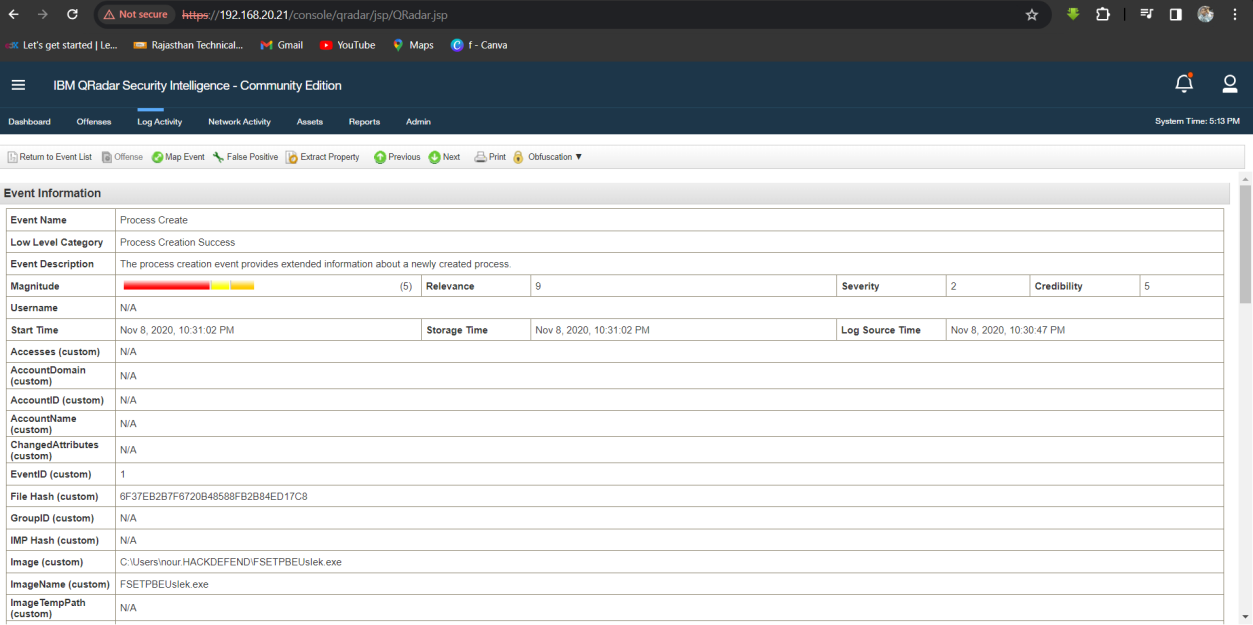
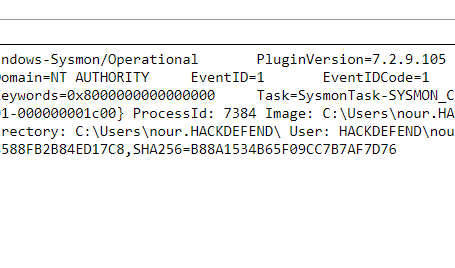
Q19. What is the PID of the process that performed injection?
Solution: 7384.
Step 1: Select Log Activity -> Add Filter Payload Contains is 192.168.10.15 and Event Name is Process Create.
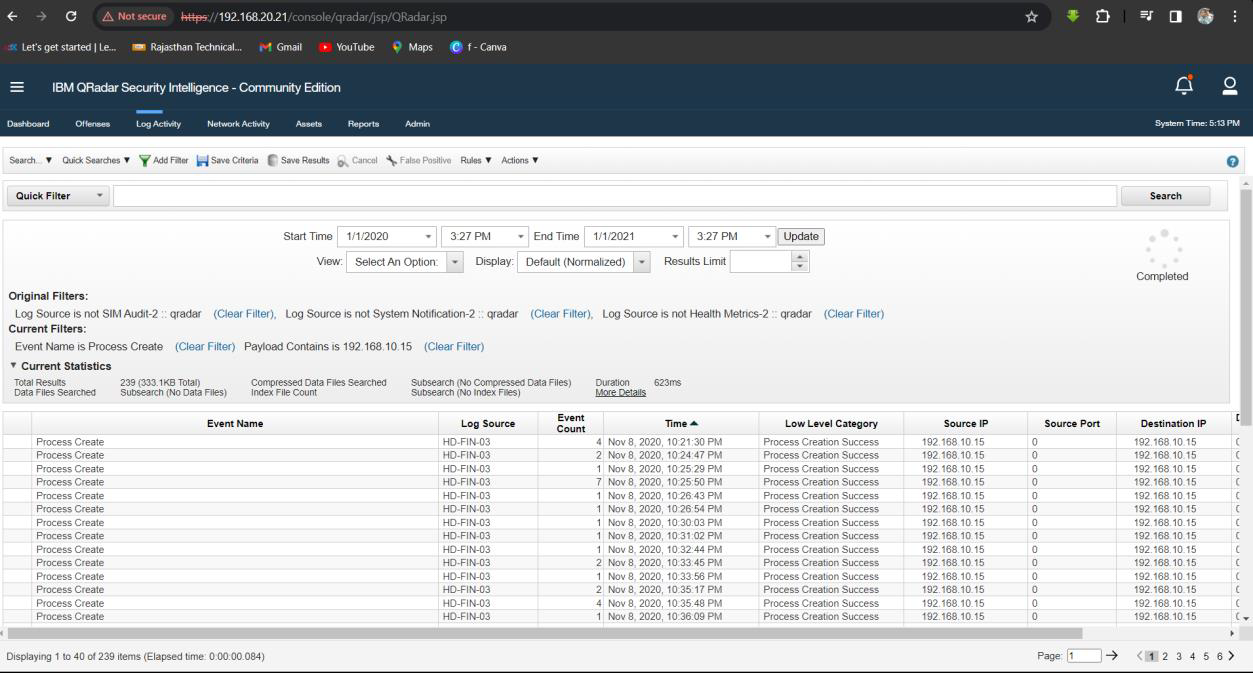
Step 2: Analyse the Log event for process ID which perform Injection.
Q20. What is the name of the tool used for lateral movement?
Solution: wmiexec.py.
Step 1: Searching on google for lateral movement tool then I found a useful GitHub Link.
https://github.com/SecureAuthCorp/impacket.
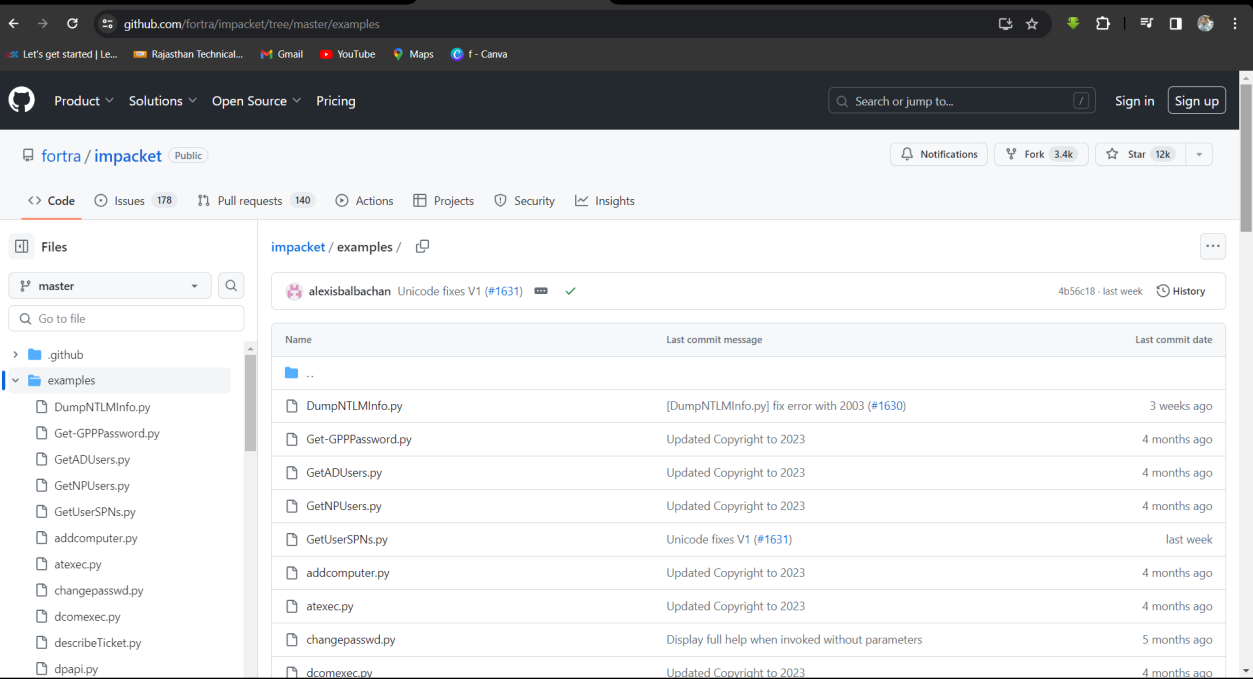
Step 2: Analyse the Github page then find the tool.
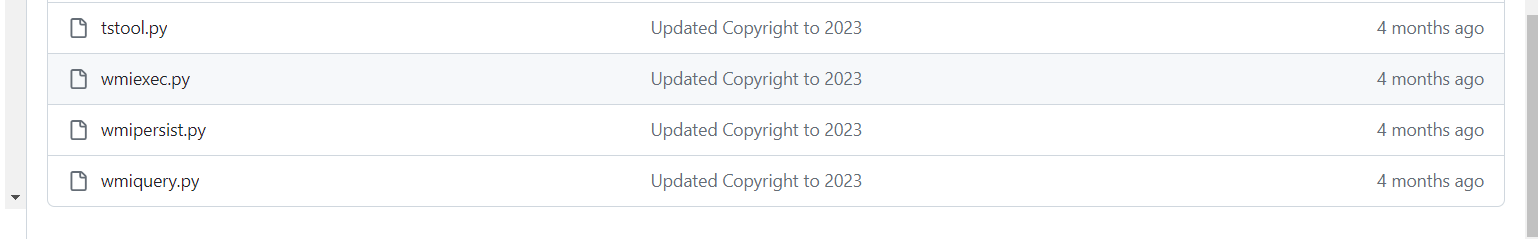
Q21. Attacker exfiltrated one file, what is the name of the tool used for exfiltration?
Solution: curl.
Step 1: Select Log Activity -> Add Filter Payload Contains is 192.20.80.25 and Log Source is not Zeek_conn.
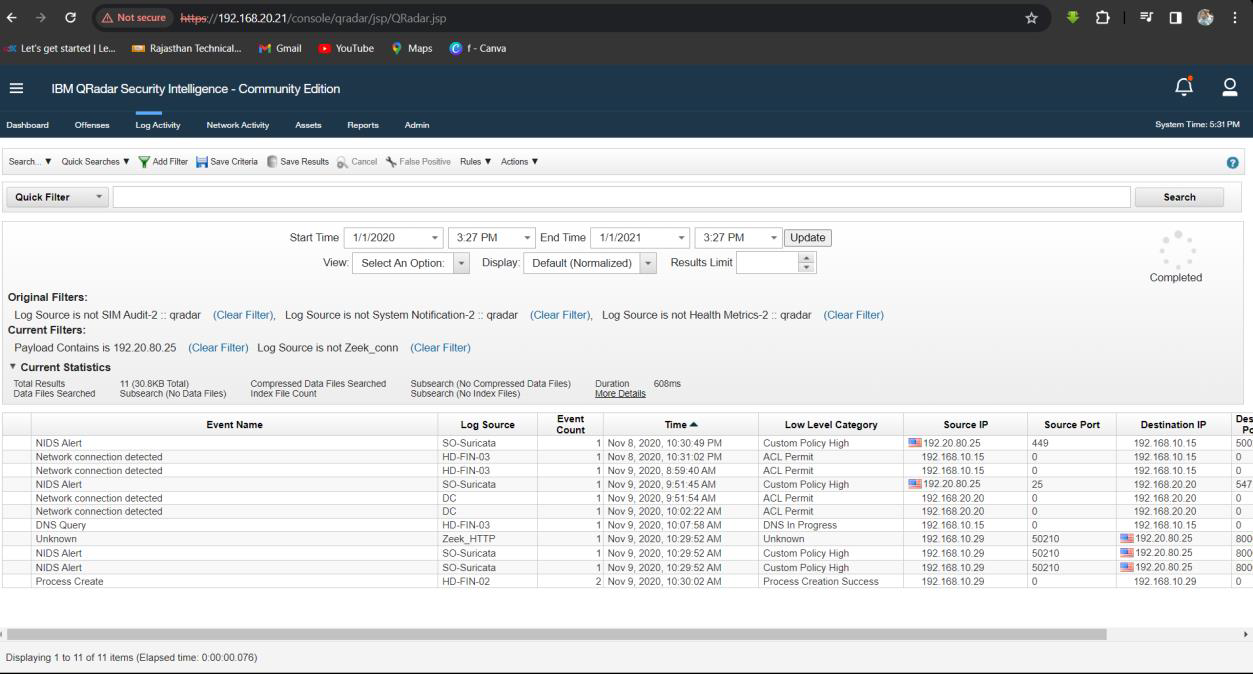
Step 2: Analyse the Log event for exfiltration tool.
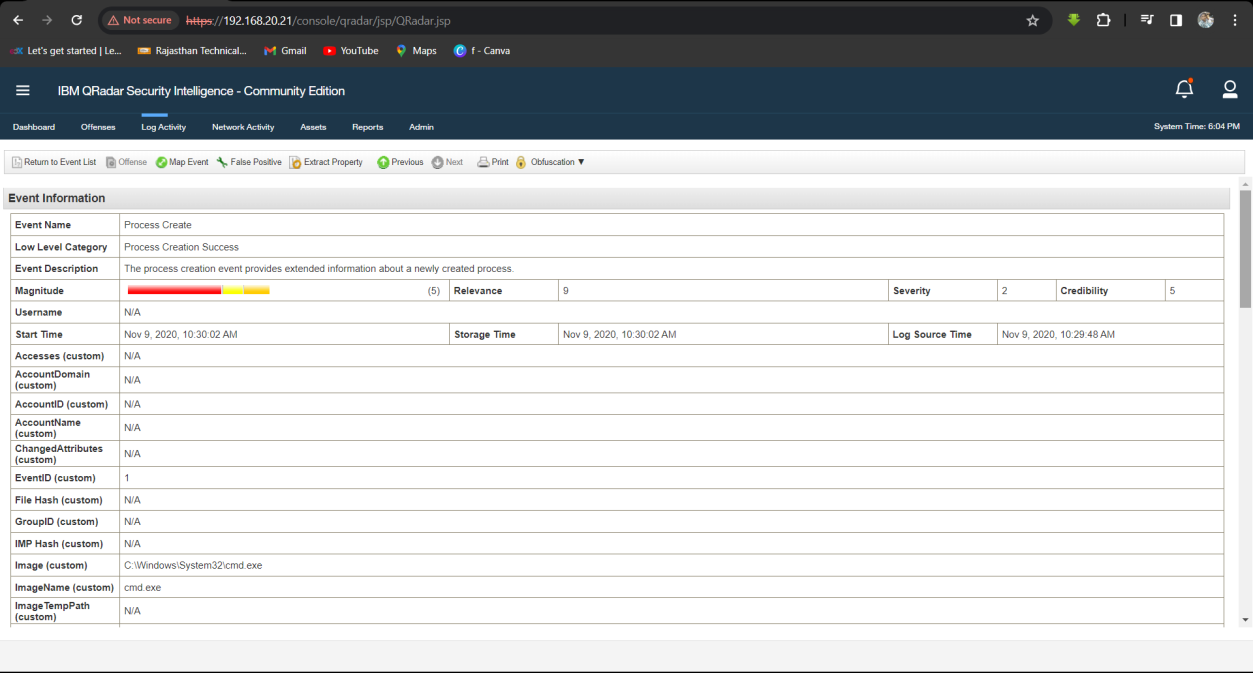
Q22. Who is the other legitimate domain admin other than the administrator?
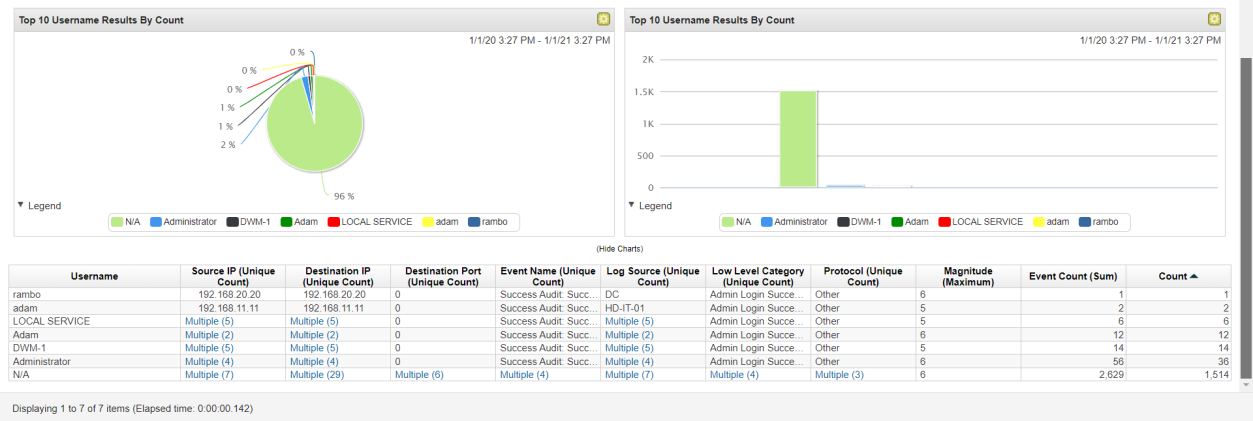
Solution: Adam.
Step 1: Select Log Activity -> Add Filter Payload Contains is 4672 and Group by username.
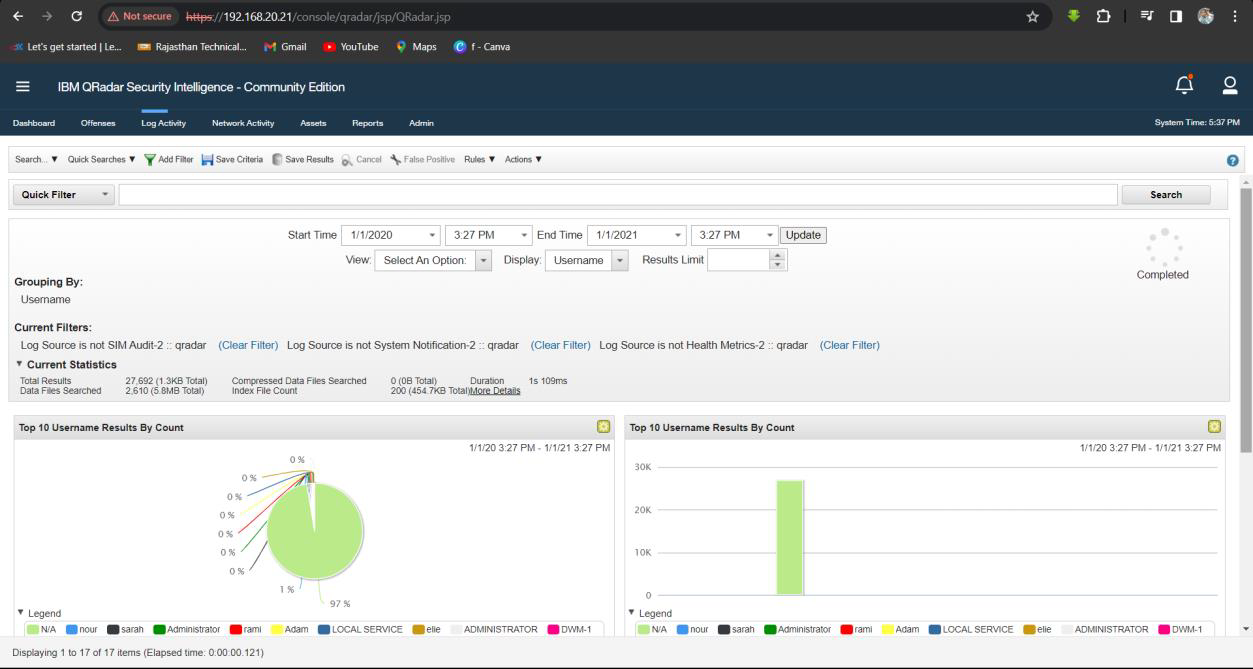
Step 2: Analyse the Username.
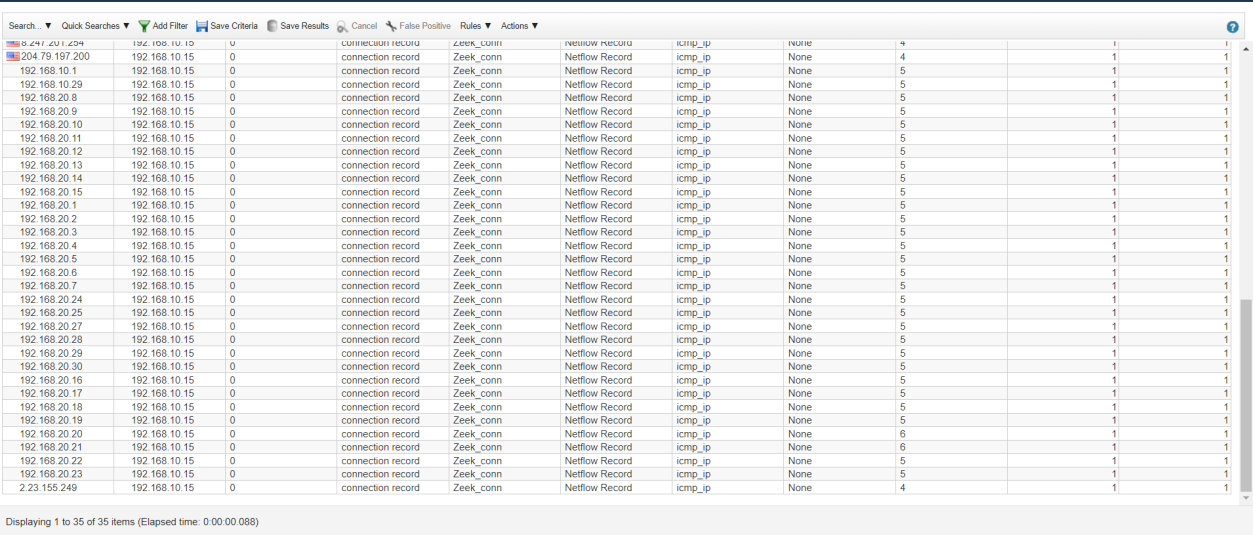
Q23. The attacker used the host discovery technique to know how many hosts available in a certain network, what is the network the hacker scanned from the host IP 1 to 30?
Solution: 192.168.20.0.
Step 1: Select Log Activity -> Add Filter Destination Port is 0, Source IP is 192.168.10.15, Log Source is Zeek_conn and Group by Destination IP.
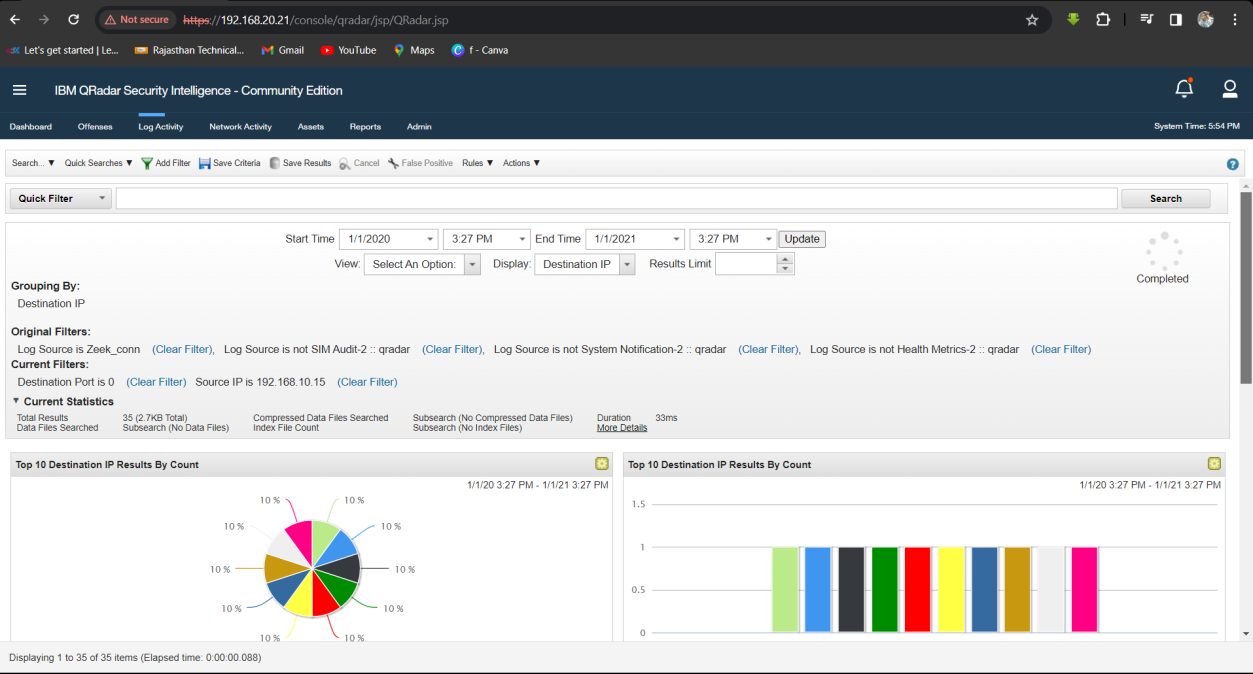
Step 2: Analyse the host IP address range 1-30.
Q24. What is the name of the employee who hired the attacker?
Solution: Sami.
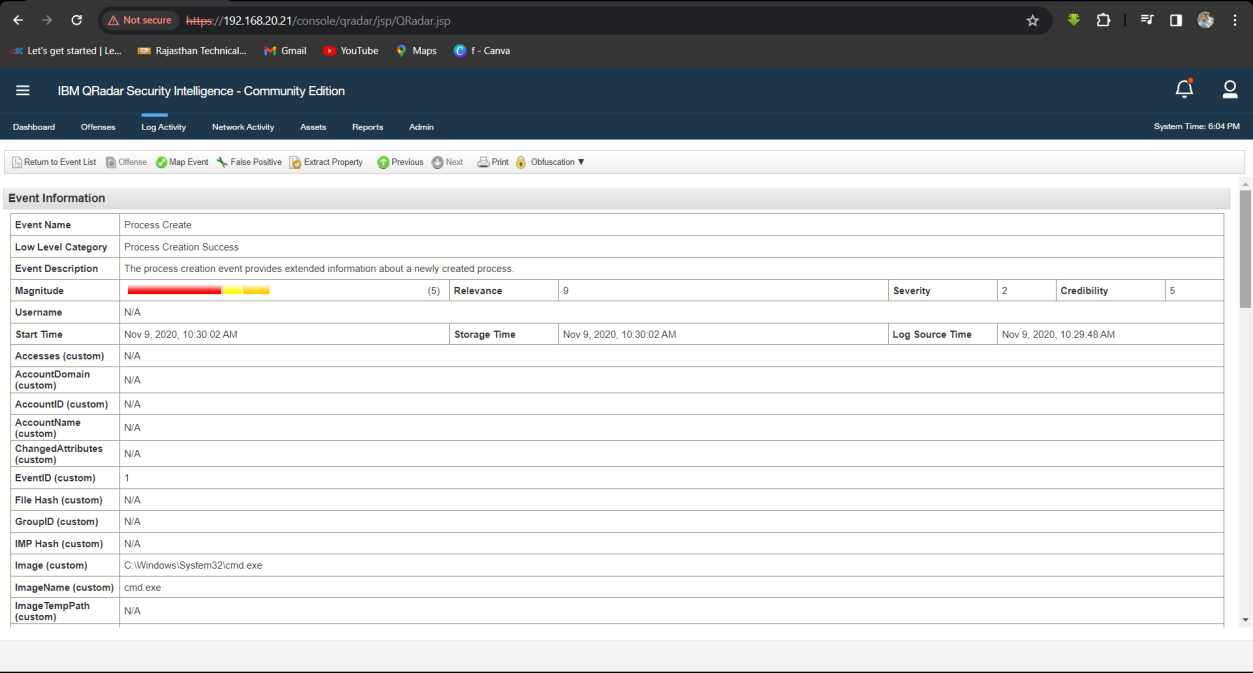
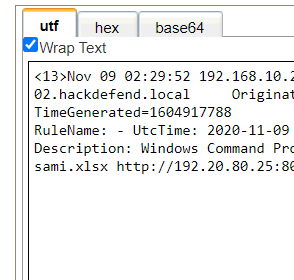
Step 1: Select Log Activity -> Add Filter Payload Contains is 192.20.80.25 and Log Source is not Zeek_conn.
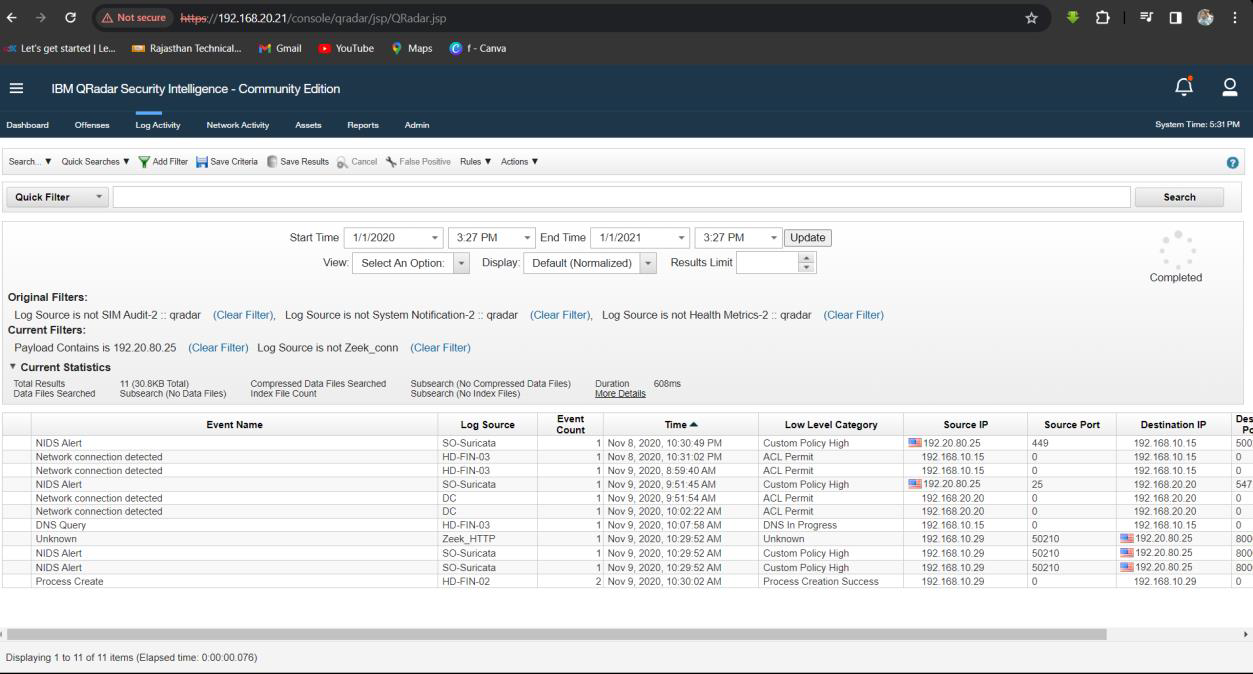
Step 2: Analyse the Log event for name of the employee who hired the attacker and noticed the suspicious sami.xlsx
spreadsheet.
Conclusion
The QRadar analysis has uncovered a comprehensive and sophisticated attack on the HACKDEFEND.local domain. The threat actor, whose IP address is 192.20.80.25, successfully compromised the internal network and executed a series of malicious activities. The investigation revealed a clear and methodical attack chain:
Initial Compromise: The attack started with a malicious file named important_instructions.docx being used as the initial vector. This file's MD5 hash, 9D08221599FCD9D35D11F9CBD6A0DEA3, links it to the initial infection. The first infected machine was 192.168.10.15, belonging to an employee named Nour.
Host and Network Discovery: The attacker, from the compromised host, used the icmp protocol to perform host discovery. This allowed them to map out the internal network, including the 192.168.20.0 subnet, to identify potential targets for lateral movement.
Persistence and Privilege Escalation: The attacker gained persistence by using the T1547.001 technique (Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder). They also created a new account named Rambo to maintain access and elevated privileges. The attacker also checked if PowerShell logging was enabled, likely to avoid detection and ensure their commands would not be logged.
Lateral Movement and Command & Control: The attacker used the wmiexec.py tool for lateral movement to target other systems, including MGNT-01, in an attempt to cover their tracks. They established a C&C channel, with the first malicious connection to the domain controller occurring at 11:14:10.
Data Exfiltration: The final stage of the attack involved exfiltrating sensitive data. The attacker targeted a specific company project, project48, and used the curl tool to transfer the stolen files. The malicious activity was orchestrated by a user named Sami, who appears to have hired the attacker, as indicated by a suspicious file named sami.xlsx.
This challenge provides a practical demonstration of how a SIEM platform like QRadar can be used to piece together a complex security incident. By correlating logs from multiple sources, a security analyst can identify the full scope of an attack, understand the tactics used by the threat actor, and recommend appropriate remediation measures. The findings from this investigation are critical for incident response and for improving the overall security posture of the organization.